A new rotation of artworks was recently installed in the Barrel Vault, our main contemporary art space. Included in this new installation are masterpieces by Jackson Pollock, Lee Krasner, and Hans Hofmann, as well as several newly acquired artworks. One of the highlights of the gallery is Robert Smithson’s Mirrors and Shelly Sand. The work is composed of approximately three tons of sand and 50 mirrors (glued back-to-back in pairs of two) lined up in a row, creating the illusion of infinity when you gaze into them. This engaging piece invites the viewer in and encourages interaction (but just of the mental variety—please remember not to touch!).
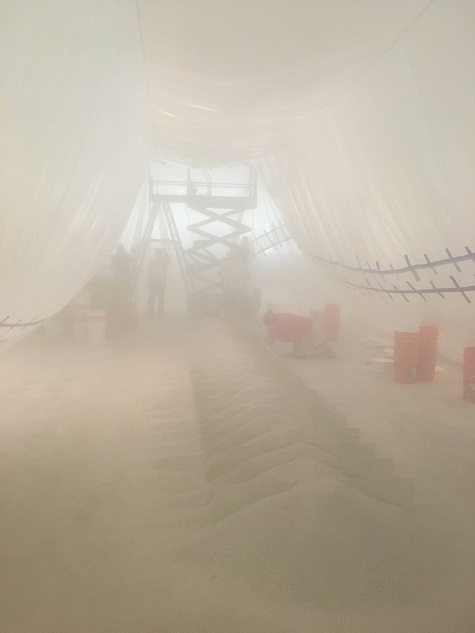
The piece becomes even more interesting when you know the process required to install it. It takes a lot of work and skill to transform the 125 buckets of sand and two crates of mirrors into the finished work of art. There are specific instructions from the artist on how the piece should be installed, but there will always be variances due to the nature of the materials. Thankfully for us, one of our Senior Preparators, Mary Nicolett, has installed the Smithson eight times and is a pro.
First our crew constructs a massive tent made of plastic. This keeps all of the sand contained and ensures that other artworks in the area are protected. On installation day, our stellar team of preparators (professional art handlers) put on their protective gear and prepare to get dirty. After the Registrar (me!) completes a condition report on all the mirrors, they are lined up based on the artist’s specifications and a small pile of sand is poured over them to keep them in place. Once all of the mirrors are in place, the real fun begins. Each preparator grabs a bucket of sand and begins pouring. Once all the buckets are empty, Nicolett begins smoothing the sand into the appropriate shape. At the end of the day, the dusty crew exits the tent to let the dust settle. The next day, the tent is removed and the finishing touches to the sand are completed.
Installation works like Mirrors and Shelly Sand allow our prep team to flex their creative muscles. While we do follow the instructions provided by the artist, the preparators are the ones who physically create the artwork as you see it. A good prep team is vital to any art institution as they are the ones who know the intricacies of a piece and how to safely install it. Thankfully for us, we have one of the best!
Katie Province is the Assistant Registrar for Collections and Exhibitions at the DMA.