This week the DMA’s beloved Late Night program turns sixteen! In celebration of each year the program has been around, let’s take a look at artworks that were added to the permanent collection during those years—they are also currently on display, so be sure to keep a lookout for them when you’re here for Late Night!
2004
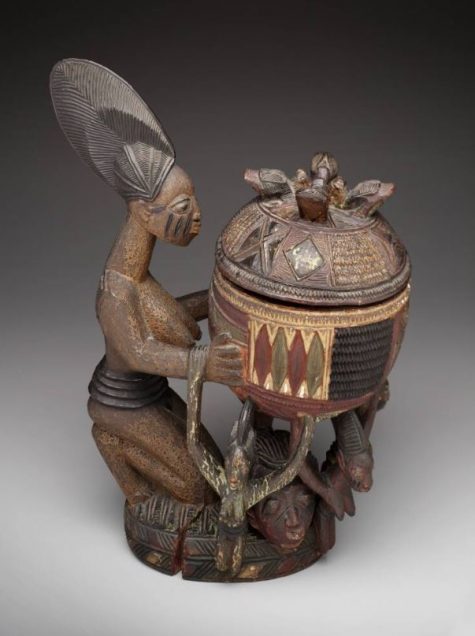

Olowe of Ise, Kneeling female figure with bowl (olumeye), Nigeria, c. 1910-c. 1938, wood, pigment, and paint, Dallas Museum of Art, The Eugene and Margaret McDermott Art Fund, Inc., 2004.16.McD
2005

Sugar bowl, Lebolt & Co., Chicago, Illinois, c. 1915, silver, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Marguerite and Robert K. Hoffman in honor of Nancy Hamon, 2005.51.5.a-b
2006
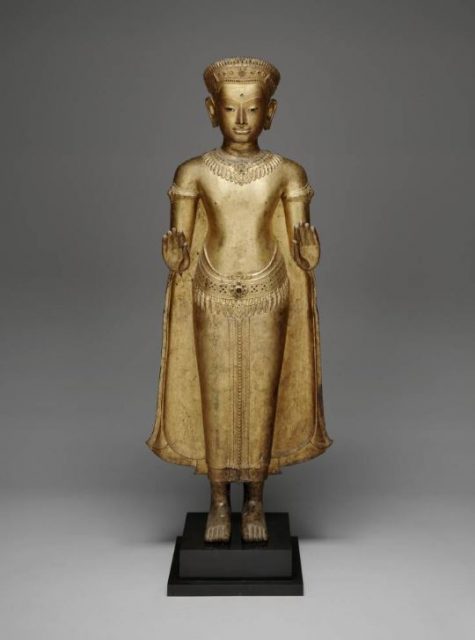

Buddha Sakyamuni, Thailand, Khmer, c. 13th century, gilded bronze, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of David T. Owsley via the Alvin and Lucy Owsley Foundation, the Cecil and Ida Green Acquisition Fund, and Bromberg Family Wendover Fund, 2006.21
2007

Mark Handforth, Dallas Snake, 2007, steel, aluminum, and glass lamp head, Dallas Museum of Art, TWO x TWO for AIDS and Art Fund and Lay Family Acquisition Fund, 2007.39
2008
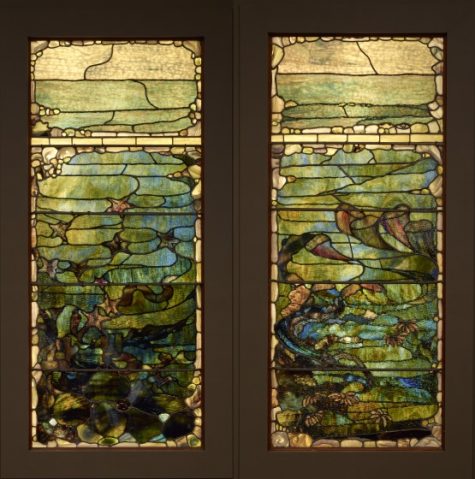

Window with Sea Anemone (“Summer”), Louis Comfort Tiffany (designer), Tiffany Glass and Decorating Company (manufacturer), New York, New York, c. 1885-95, glass, lead, iron, and wooden frame (original), Dallas Museum of Art, The Eugene and Margaret McDermott Art Fund, Inc., 2008.21.1.McD
2009
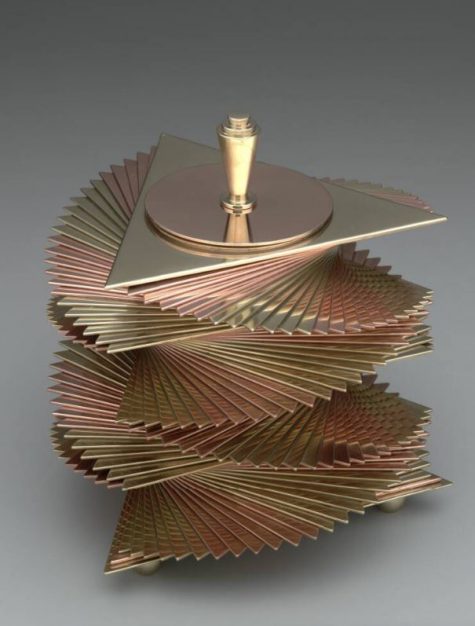
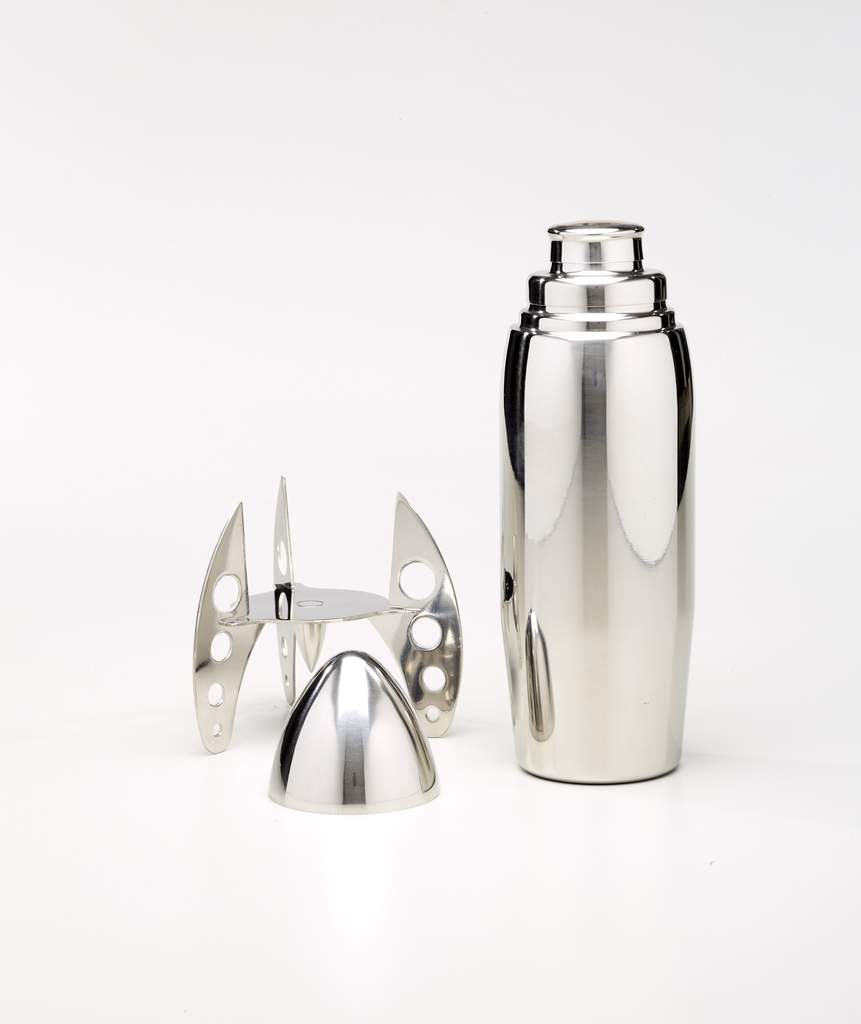
Box, John Nicholas Otar (designer), c. 1933, copper and brass, Dallas Museum of Art, Discretionary Decorative Arts Fund, 2009.7.a-b
2010

Nandi, India, c. 13th century, granite, Dallas Museum of Art, the Cecil and Ida Green Acquisition Fund and gift of David T. Owsley via the Alvin and Lucy Owsley Foundation, 2010.6
2011

François-Auguste Biard, Seasickness on an English Corvette, 1857, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of J. E. R. Chilton, 2011.27
2012

Marriage necklace, India, Tamil Nadu, late 19th century, gold, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of David T. Owsley honoring Dr. Anne Bromberg via the Alvin and Lucy Owsley Foundation and the Cecil and Ida Green Acquisition Fund, 2012.46
2013

Guillaume Lethière, Erminia and the Shepherds, 1795, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, Foundation for the Arts Collection, Mrs. John B. O’Hara Fund, 2013.1.FA
2014

Antoine-Augustin Préault, Silence, c. 1842, patinated plaster, Dallas Museum of Art, The Mr. and Mrs. George A. Shutt Fund and General Acquisitions Fund, 2014.10
2015
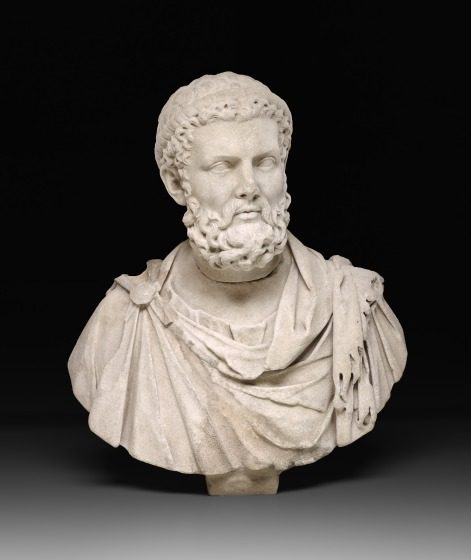

Bust of Herakles, Roman, Lambert Sigisbert Adam (restorer), 1st century-2nd century CE, marble, Dallas Museum of Art, the Cecil and Ida Green Acquisition Fund, gift of David T. Owsley via the Alvin and Lucy Owsley Foundation, and Bromberg Family Wendover Fund, 2015.31
2016
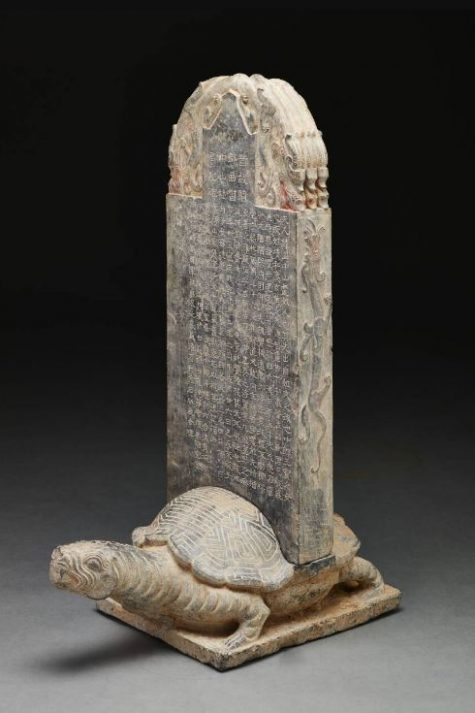

Tomb plaque marker on a tortoise base, China, c. 219-c. 316 CE, limestone, Dallas Museum of Art, the Cecil and Ida Green Acquisition Fund, 2016.33.a-b
2017

Jonas Wood, Untitled (Big Yellow One), 2010, oil on linen, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Vernon and Amy Faulconer, 2017.45.2, © Jonas Wood
2018

Pair of six-panel folding screens depicting “The Tale of Genji,” Japan, Kano School, 16th-17th century, ink and color on paper, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of David T. Owsley via the Alvin and Lucy Owsley Foundation, Bromberg Family Wendover Fund, and the Cecil and Ida Green Acquisition Fund, 2018.21.1-2
Valerie Chang is the McDermott Intern for Adult Programming at the DMA.
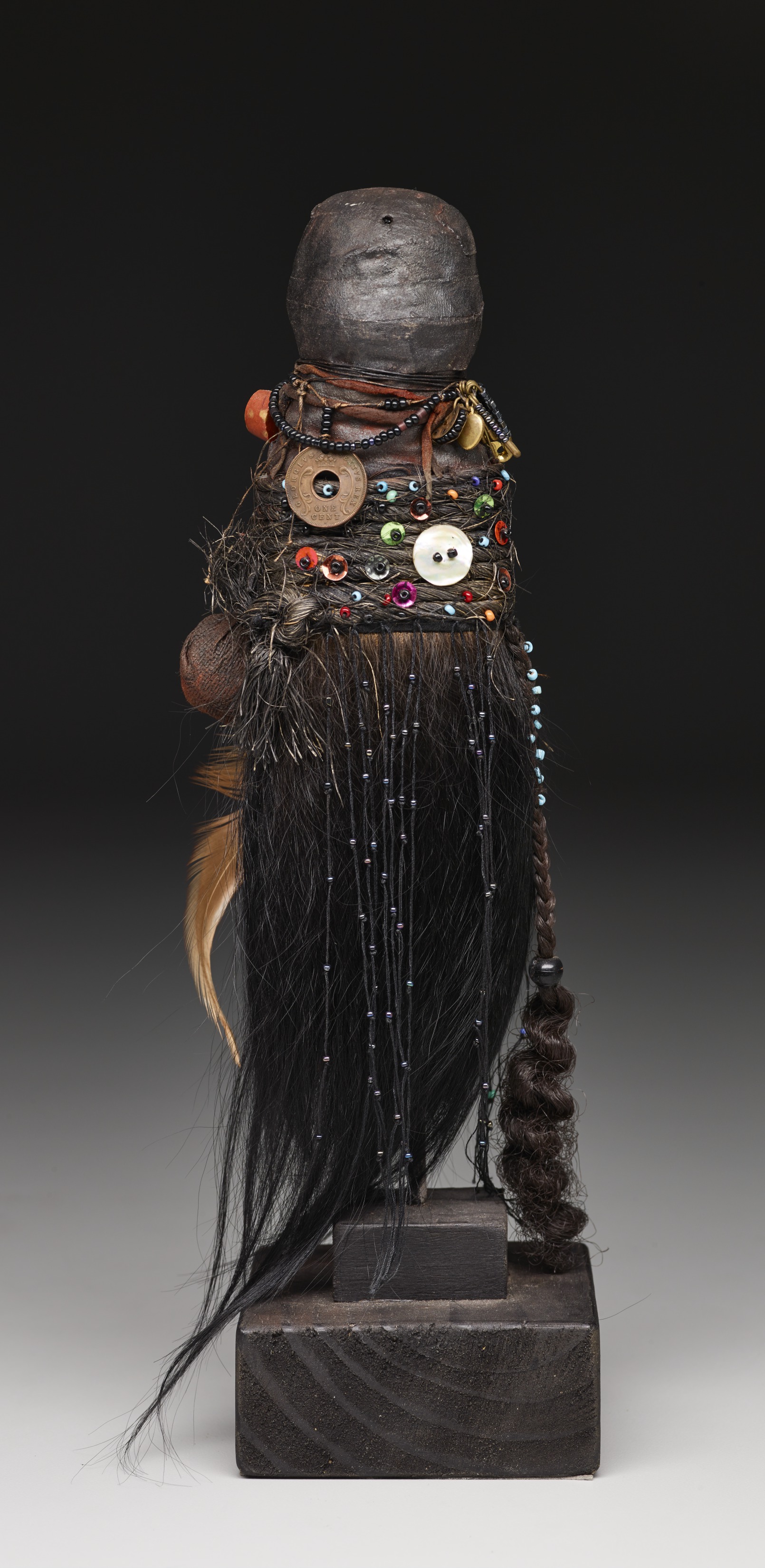





























 Renee Stout, Fetish #1, 1987, monkey hair, nails, beads, cowrie shells, and coins, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Roslyn and Brooks Fitch, Gary Houston, Pamela Ice, Sharon and Lazette Jackson, Maureen McKenna, Aaronetta and Joseph Pierce, Matilda and Hugh Robinson, and Rosalyn Story in honor of Virginia Wardlaw, 1989.128, © Renee Stout, Washington, D.C.
Renee Stout, Fetish #1, 1987, monkey hair, nails, beads, cowrie shells, and coins, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Roslyn and Brooks Fitch, Gary Houston, Pamela Ice, Sharon and Lazette Jackson, Maureen McKenna, Aaronetta and Joseph Pierce, Matilda and Hugh Robinson, and Rosalyn Story in honor of Virginia Wardlaw, 1989.128, © Renee Stout, Washington, D.C.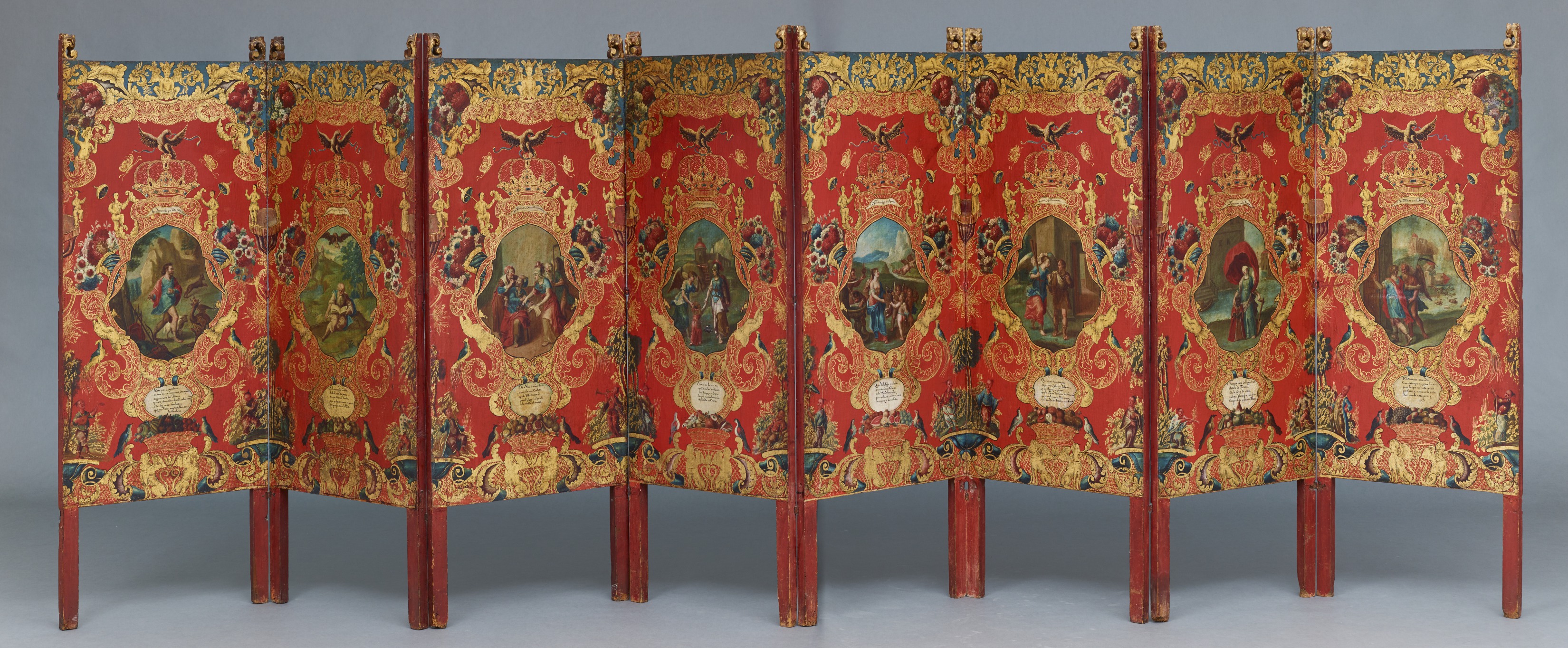 Screen, Mexico, Mexico City, c. 1740–60, oil on canvas, pine, and gilding, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of the Stanley and Linda Marcus Foundation, 1993.74.a-b
Screen, Mexico, Mexico City, c. 1740–60, oil on canvas, pine, and gilding, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of the Stanley and Linda Marcus Foundation, 1993.74.a-b
 John McCrady, Wreck of the Old 97, date unknown, lithograph, Dallas Museum of Art, Dallas Art Association Purchase, 1948.6
John McCrady, Wreck of the Old 97, date unknown, lithograph, Dallas Museum of Art, Dallas Art Association Purchase, 1948.6
 Cabinet on stand, Pierre Gole, Paris (?), France, 1660–80, wood, ivory, tortoiseshell, shell, and gilt bronze, Dallas Museum of Art, The Wendy and Emery Reves Collection, 1985.R.573.a-c
Cabinet on stand, Pierre Gole, Paris (?), France, 1660–80, wood, ivory, tortoiseshell, shell, and gilt bronze, Dallas Museum of Art, The Wendy and Emery Reves Collection, 1985.R.573.a-c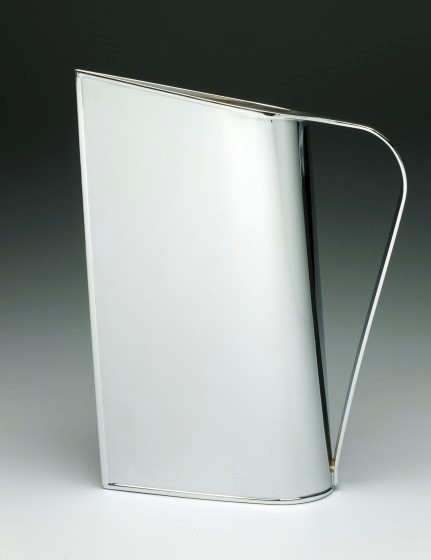 Normandie shape pitcher, Peter Muller-Munk, Rome, New York, 1935, chrome-plated brass, Dallas Museum of Art, 20th Century Design Fund, 1996.27
Normandie shape pitcher, Peter Muller-Munk, Rome, New York, 1935, chrome-plated brass, Dallas Museum of Art, 20th Century Design Fund, 1996.27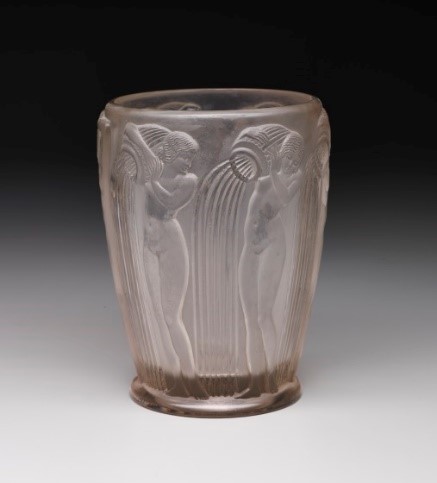 Danaides vase, René Jules Lalique, Lalique et Cie, Cristallerie, Wingen-sur-Moder, France, c. 1926, molded glass, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Mr. and Mrs. Michael Steinberg, 2004.48.5
Danaides vase, René Jules Lalique, Lalique et Cie, Cristallerie, Wingen-sur-Moder, France, c. 1926, molded glass, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Mr. and Mrs. Michael Steinberg, 2004.48.5
 Portrait head of a young woman, Roman, 2nd century CE, marble,
Portrait head of a young woman, Roman, 2nd century CE, marble, Jackson Pollock, Cathedral, 1947, enamel and aluminum paint on canvas,
Jackson Pollock, Cathedral, 1947, enamel and aluminum paint on canvas,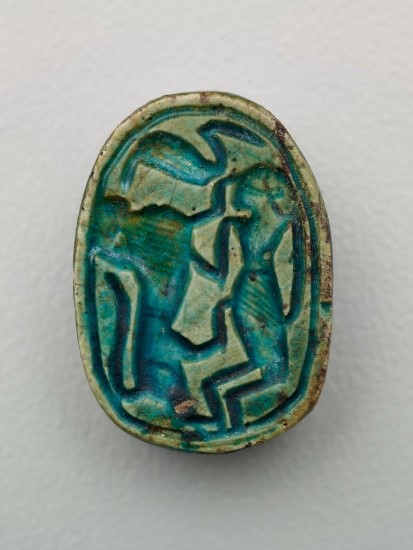 Scarab, Egyptian, 1785–1550 BCE, faience, Dallas Museum of Art, given in memory of Jerry L. Abramson by his estate, 2009.25.4
Scarab, Egyptian, 1785–1550 BCE, faience, Dallas Museum of Art, given in memory of Jerry L. Abramson by his estate, 2009.25.4
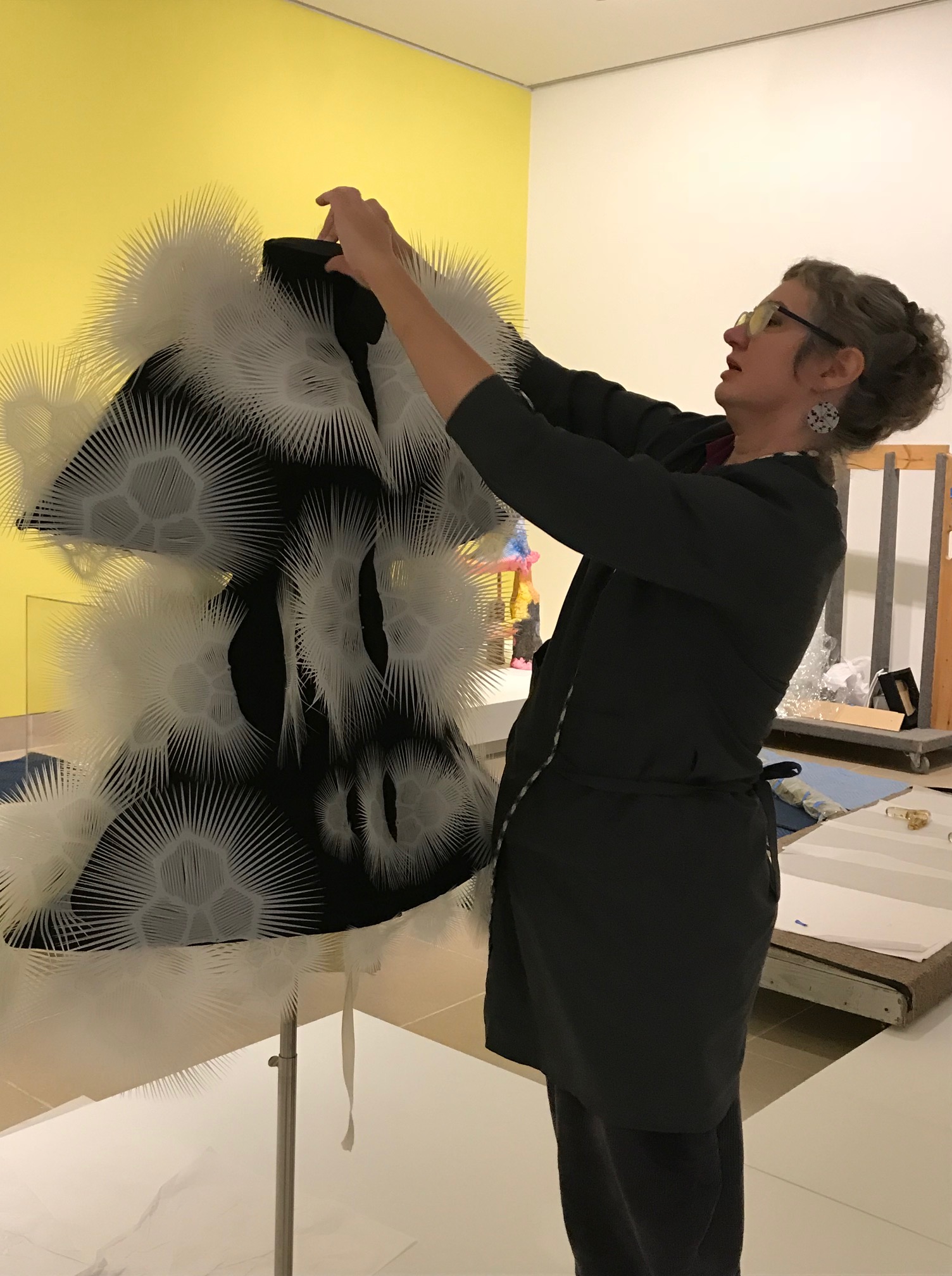























 Objects Conservator Fran Baas adjusts the laser-cut polyester lace on Iris van Herpen’s Voltage Dress.
Objects Conservator Fran Baas adjusts the laser-cut polyester lace on Iris van Herpen’s Voltage Dress.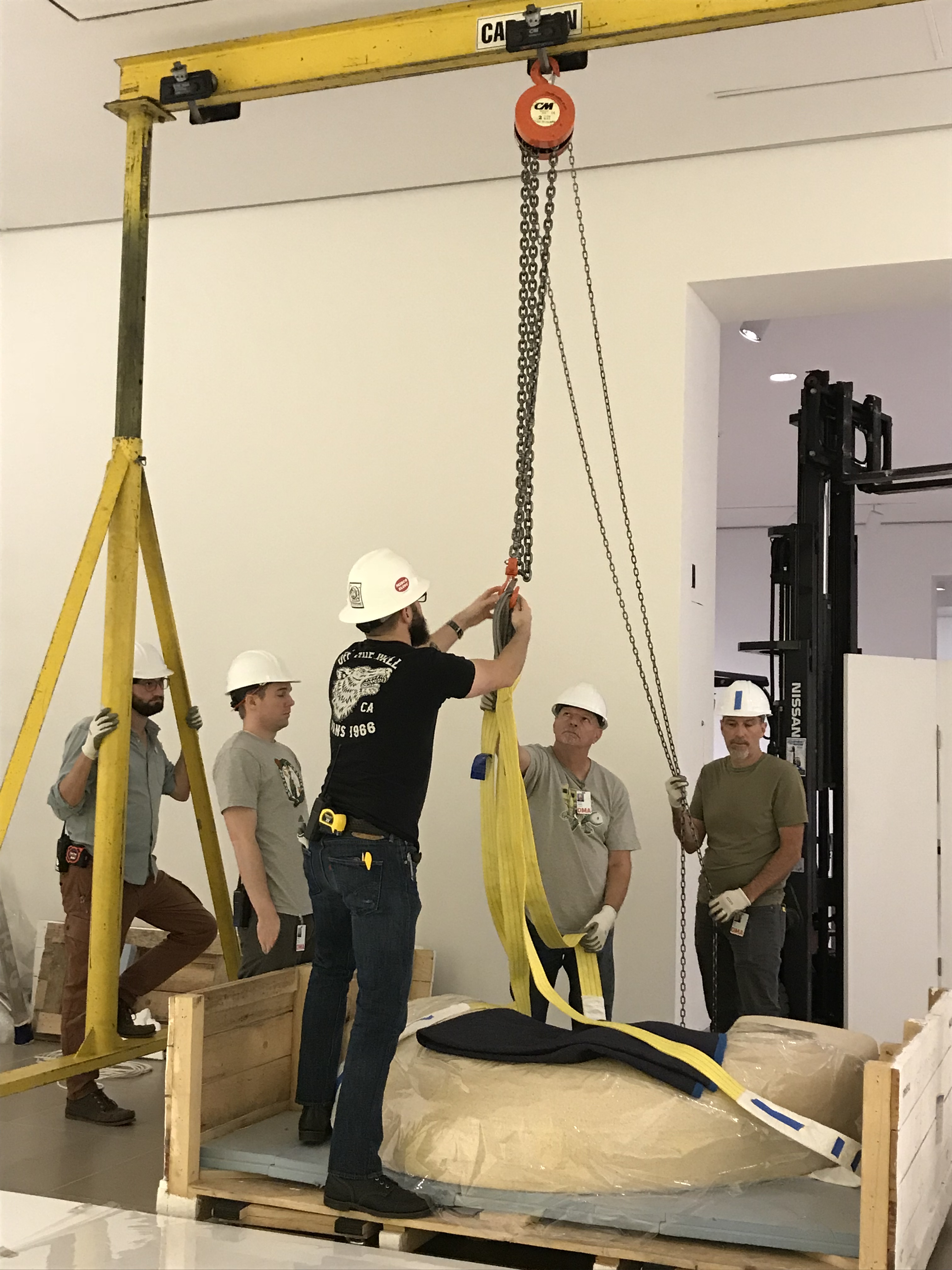 A team of preparators works on lowering the two pieces of Najla El Zein’s Seduction onto the platform. Each piece of the sculpture weighs approximately 1,500 pounds and needs to be moved with a gantry crane. The lower stone was placed first, and then the upper stone had to be carefully lowered onto it.
A team of preparators works on lowering the two pieces of Najla El Zein’s Seduction onto the platform. Each piece of the sculpture weighs approximately 1,500 pounds and needs to be moved with a gantry crane. The lower stone was placed first, and then the upper stone had to be carefully lowered onto it.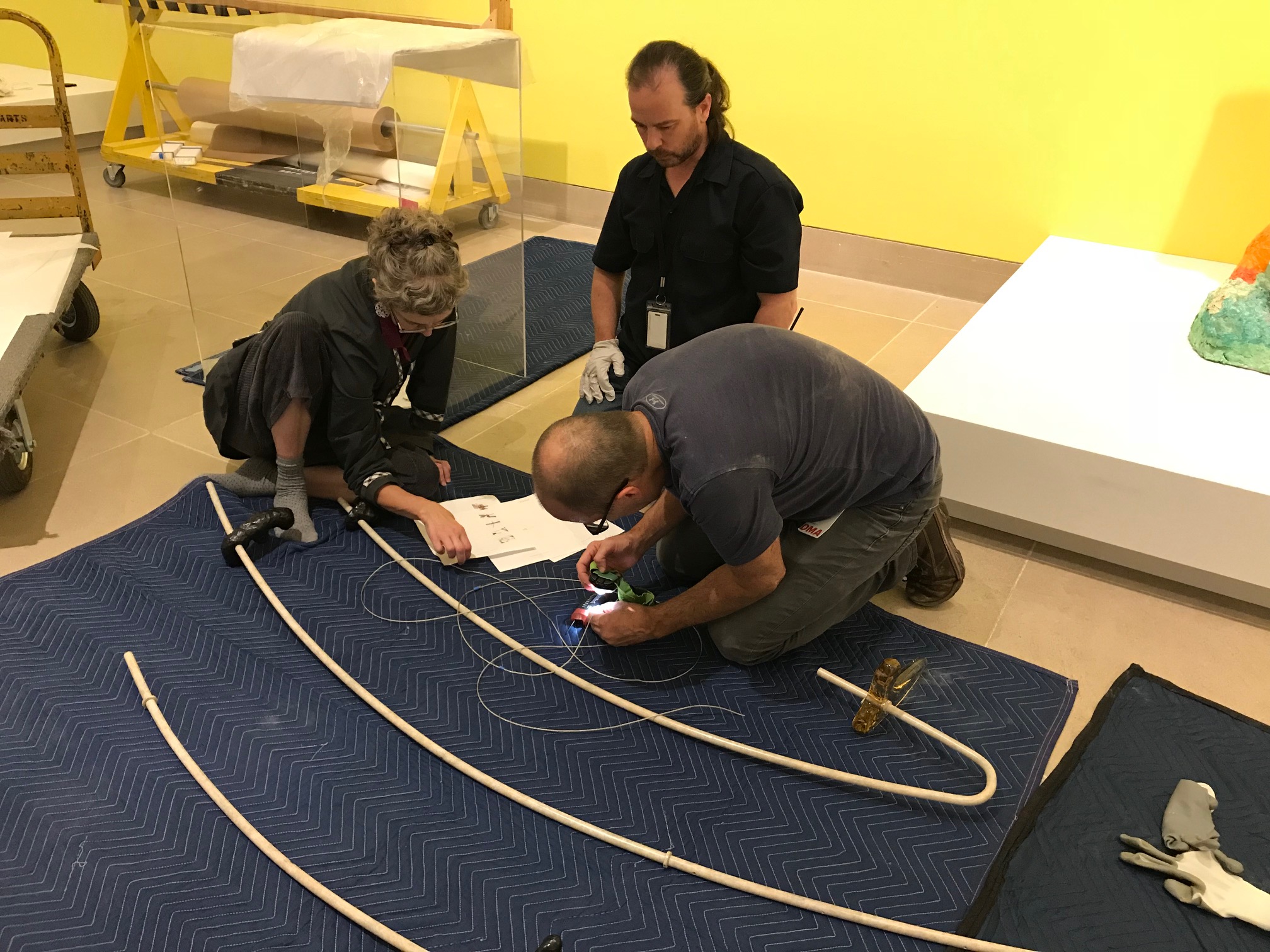 Fran Baas, Lance Lander, and Mike Hill review the instructions for assembling Faye Toogood’s Tools for Life Mobile 2. Because the components of the mobile are heavy, the team had to know exactly what to do to minimize unnecessary handling.
Fran Baas, Lance Lander, and Mike Hill review the instructions for assembling Faye Toogood’s Tools for Life Mobile 2. Because the components of the mobile are heavy, the team had to know exactly what to do to minimize unnecessary handling.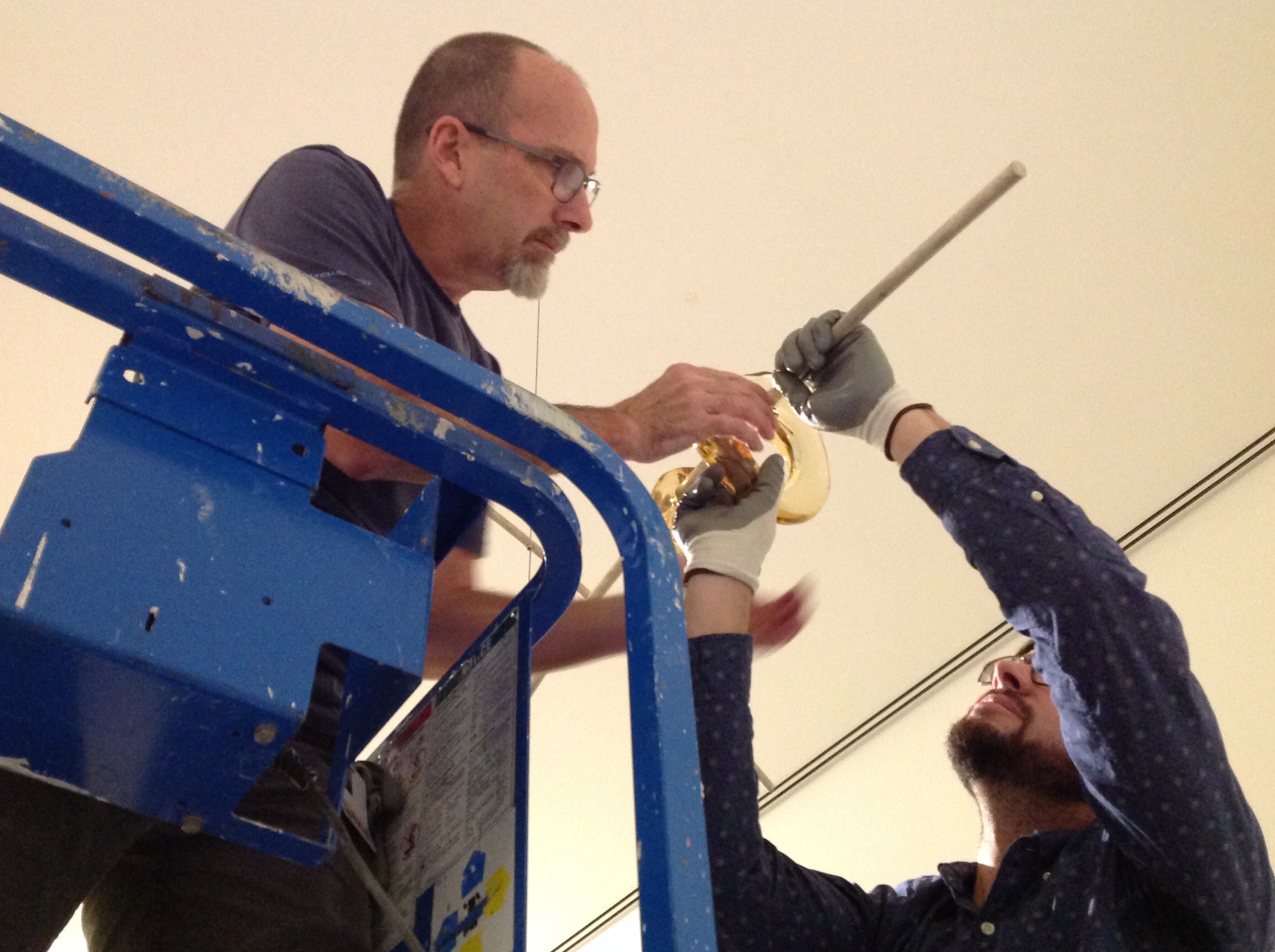 Mike Hill and John Lendvay work to assemble Tools for Life Mobile 2 as it hangs from the ceiling.
Mike Hill and John Lendvay work to assemble Tools for Life Mobile 2 as it hangs from the ceiling.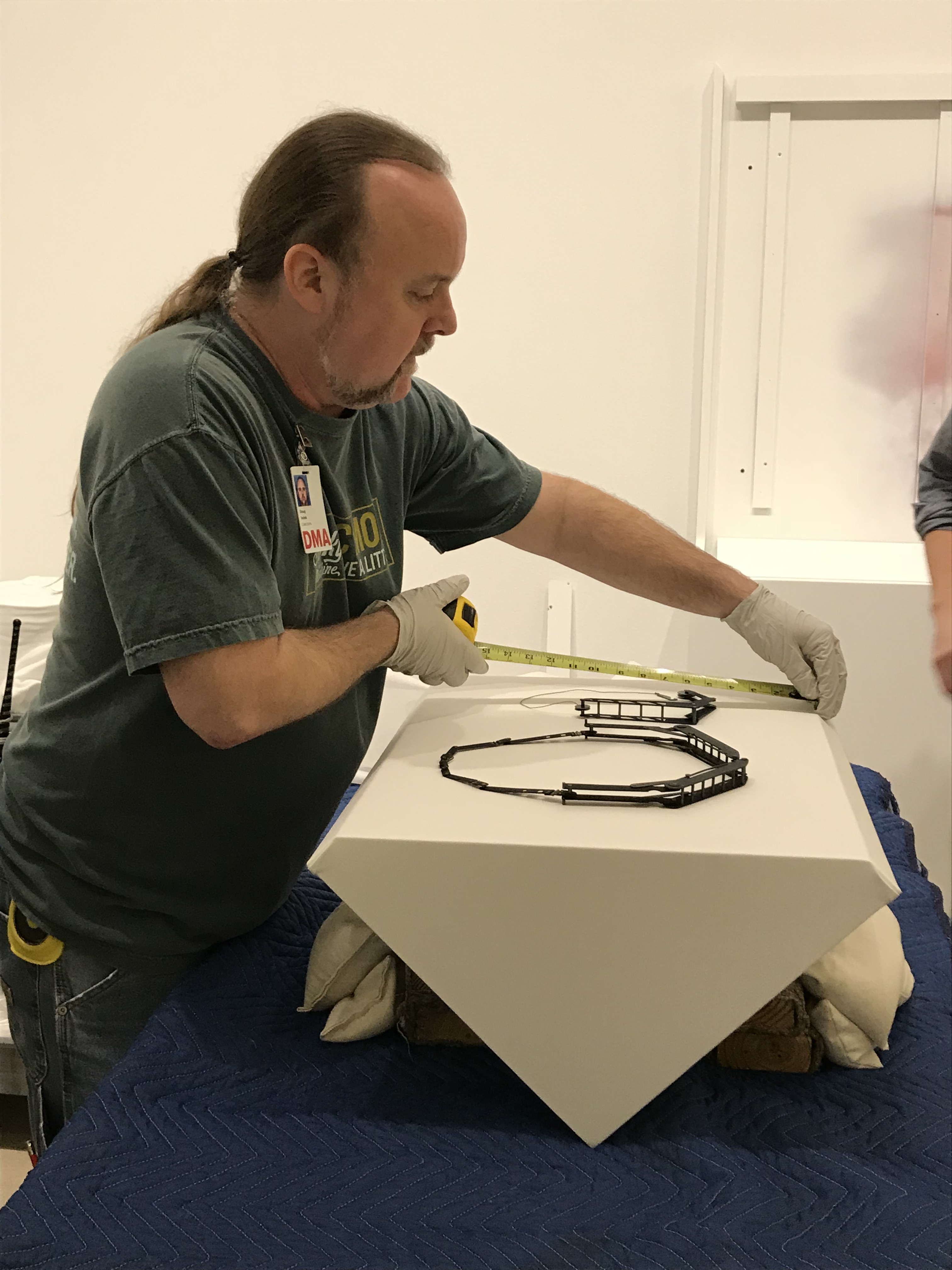 Doug Velek takes measurements for the two pieces of jewelry by Katie Collins. Prior to installing the work, the preparators made the wedges and lifts used to display the jewelry in the exhibition. After confirming that the necklaces were centered on the wedge, preparators used pins to secure them in place.
Doug Velek takes measurements for the two pieces of jewelry by Katie Collins. Prior to installing the work, the preparators made the wedges and lifts used to display the jewelry in the exhibition. After confirming that the necklaces were centered on the wedge, preparators used pins to secure them in place.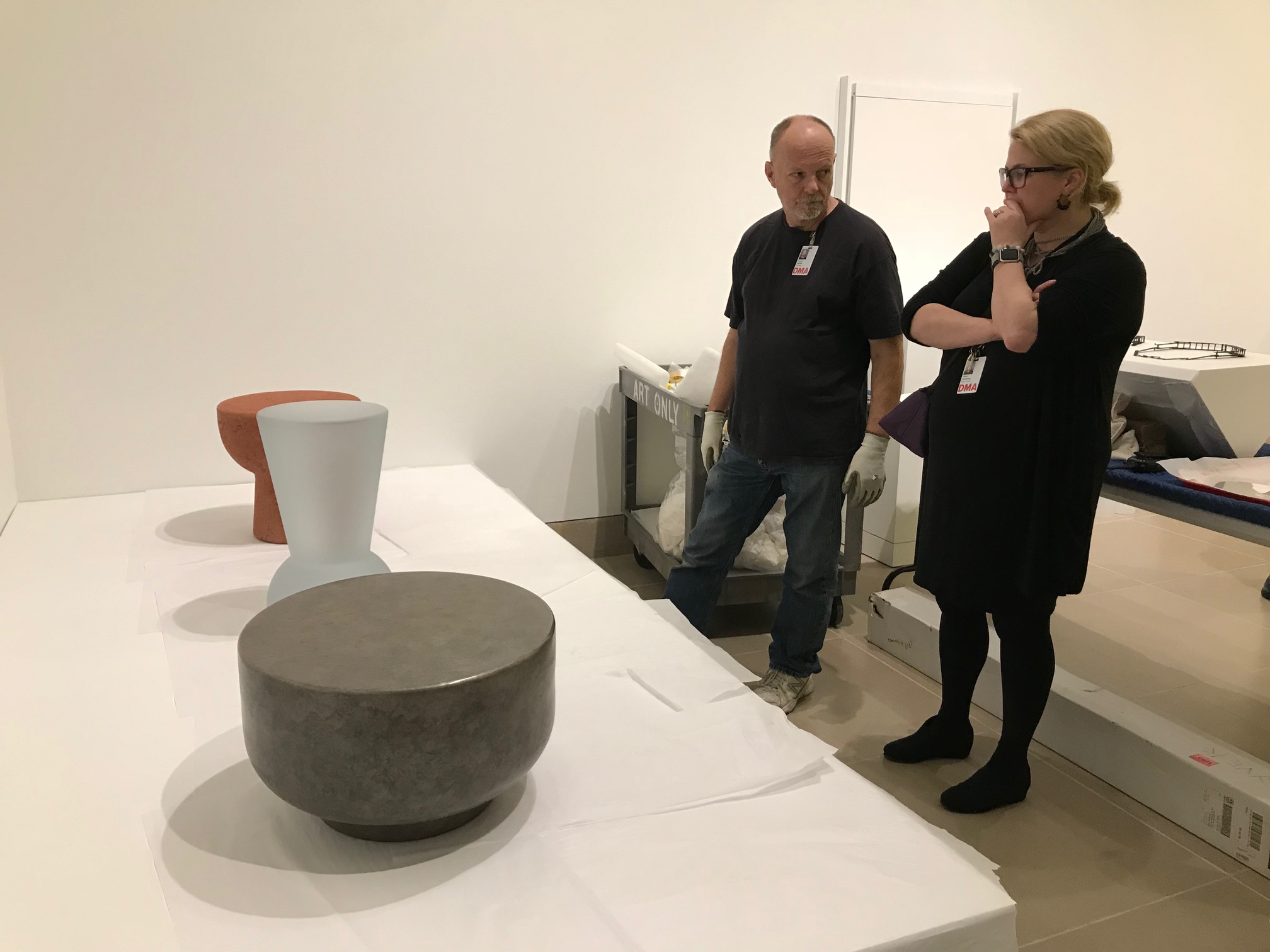 Curator Sarah Schleuning and preparator Russell Sublette discuss the placement of the three stools by Faye Toogood.
Curator Sarah Schleuning and preparator Russell Sublette discuss the placement of the three stools by Faye Toogood.



