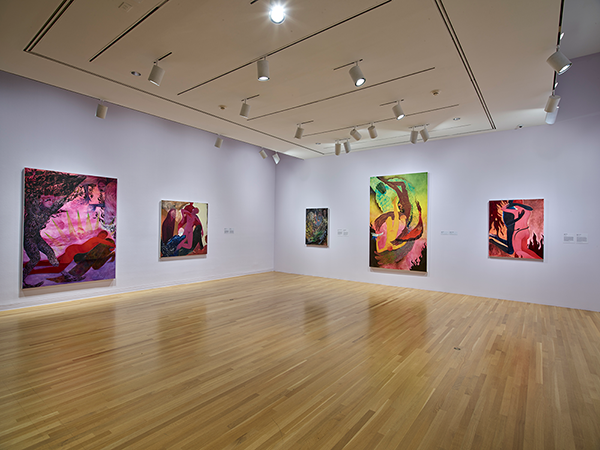
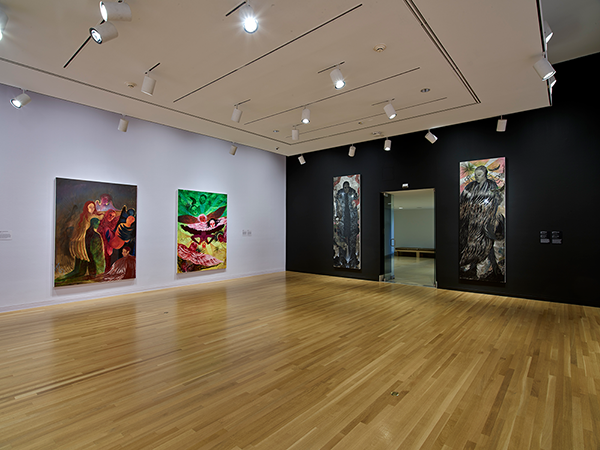
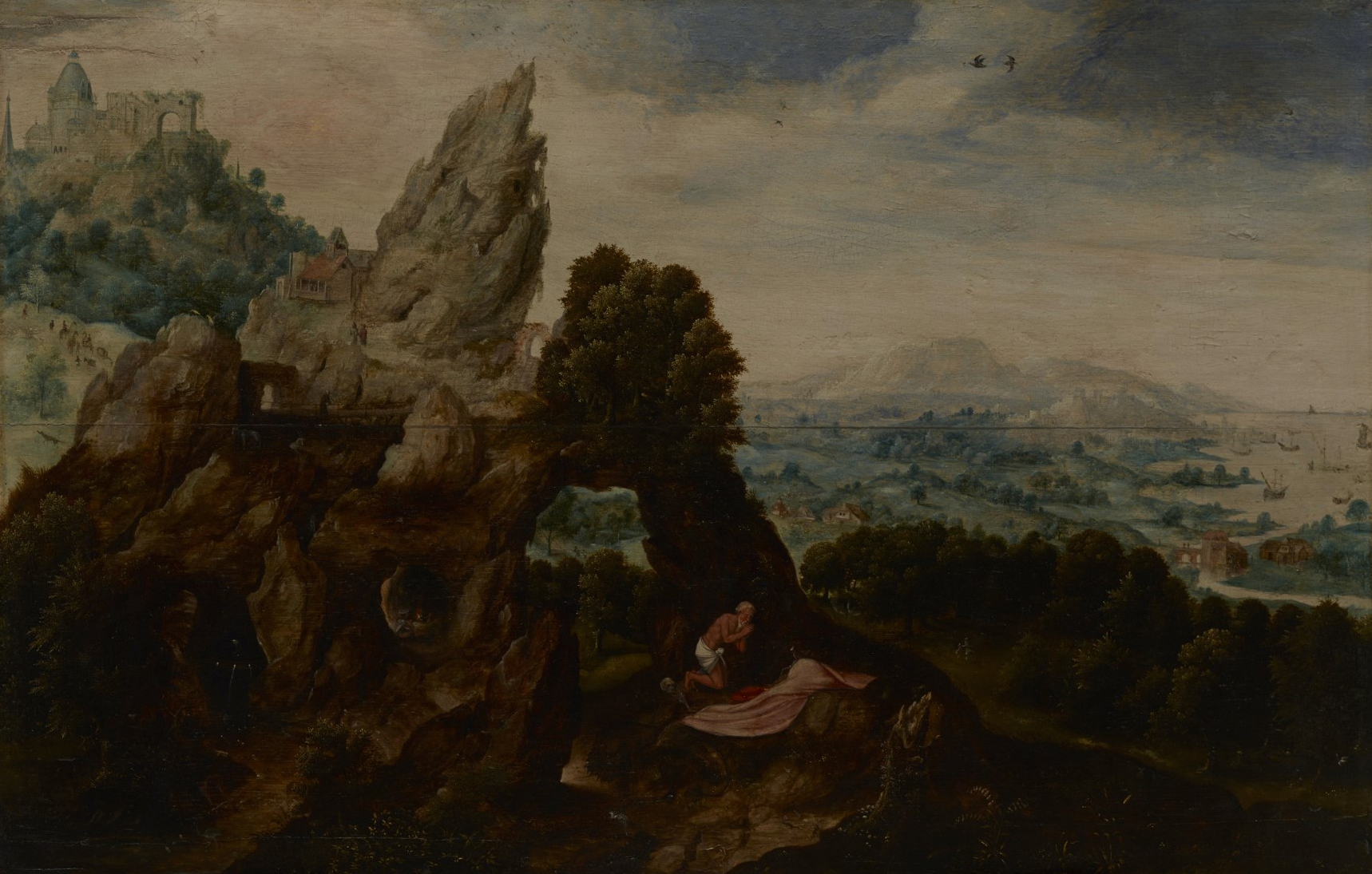
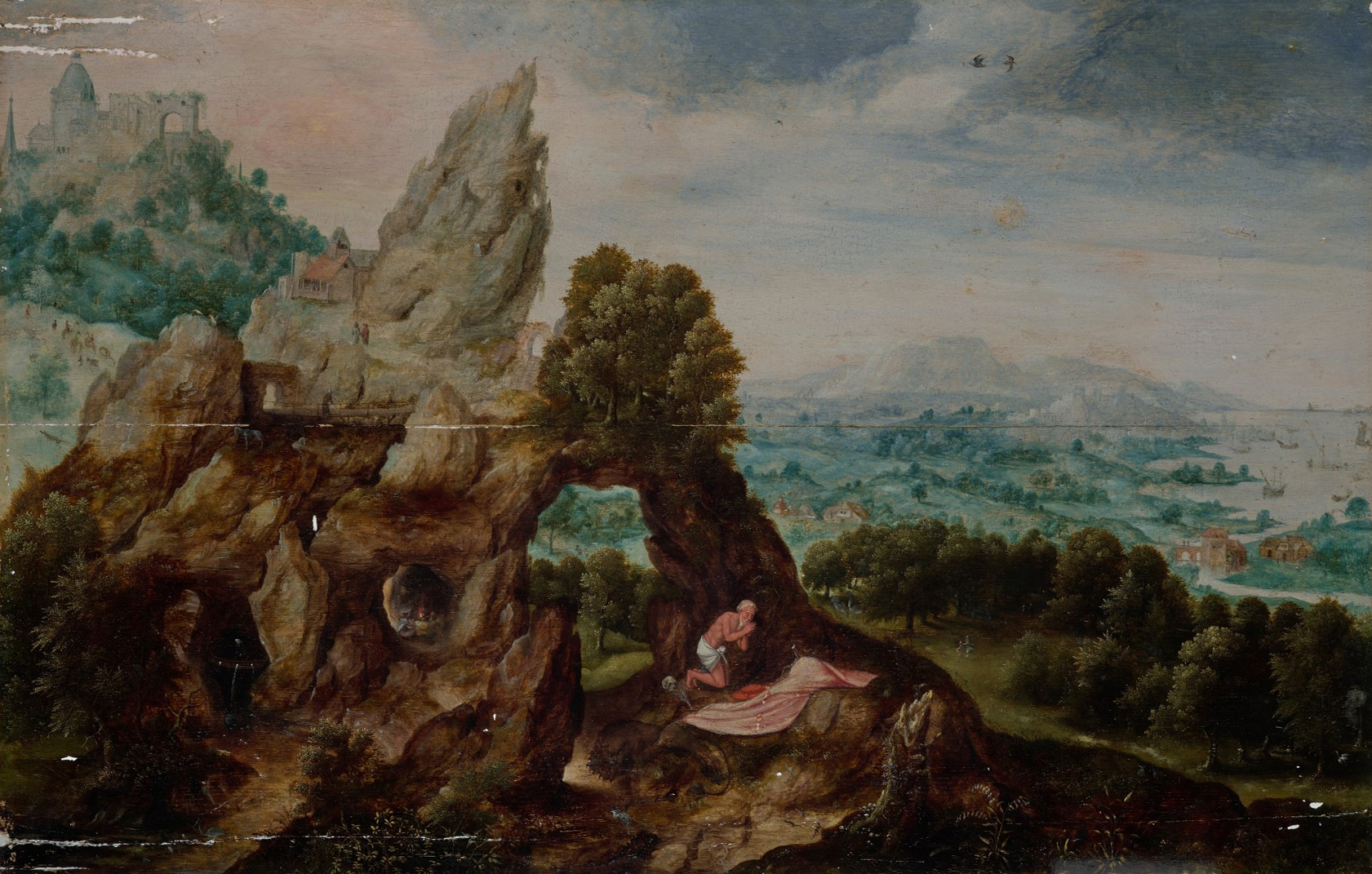
The vividly colored paintings of Brooklyn-based artist Naudline Pierre are fantastical portals to otherworldly spaces. Before Pierre’s first solo museum exhibition closes after May 15, the artist spoke with Hilde Nelson, curator of the exhibition and the DMA’s Curatorial Assistant for Contemporary Art. Read below to find out more from the interview, and don’t miss your chance to see Naudline Pierre: What Could Be Has Not Yet Appeared.
Hilde Nelson: You’ve spoken about how you see rules of light, gravity, color, etc. operating differently in your paintings. How do you see the boundaries of this world unfolding and shifting? Which conundrums are prompting the figures—and the protagonist especially—to expand?
Naudline Pierre: This world is unfolding before me––in every sense of the word. It’s allowing me glimpses of more parts of itself each time I try to dig deeper. The world can seem one way and then, all of a sudden, it appears to be another way. Many times, the figures are pictured in a sort of “nowhere,” which usually lacks a sense of a traditional foreground, middle ground, and background. However, that’s subtly changing with each new foray into this world. I think the characters in these paintings, including the protagonist herself, are facing the impact of change. Change is inevitable. These characters are feeling that inevitability, and they are accepting it. They are submitting to change, and in turn the gift they receive is expansion.
HN: In your works, the colors are often agents in themselves, operating as bearers of meaning and emotional resonance. How does color continue to take on new lives and purposes in your work?
NP: Color continues to illuminate this world in ways that I’m still exploring. What I do know is that color is a form of communication for these characters. Color is a way to communicate power, or desire, for example.
HN: In creating these other worlds, how is the surface of the painting acting as a portal for you, both materially and conceptually? Is it a point of contact? A barrier?
NP: The surface serves as both a gate and a point of contact. The surface is a skin between these two worlds. Both restriction and invitation are possible on the surface. Sometimes the surface is resisting, and sometimes it’s beckoning, guiding my hand. Ultimately, the surface is a point in my reality, something I can see and feel, that allows me to connect with these characters who exist outside of my reality.
HN: You speak about the unknown as a point of possibility in your work, but I’m interested in the ways in which the unknown can be a mode of protection and resistance for the figures in your work. How do you see elements of unknowability, opacity, and illegibility operating in your work?
NP: I see these elements of unknowability as a cloak that does in fact provide protection for these characters and their experiences. It allows them privacy to process their emotions and transformations, but also their joy and grief. They get to choose when to be known and, often, by whom. I connect this to them possessing agency and the gift of making choices that serve them. They are meeting me at the surface of the canvas saying –– may we be shielded and protected from all that isn’t meant for us. And I am saying the same.
HN: In your talk here at the DMA in September, you spoke of making as a mode of healing and told us, “All I want to do is make authentic work that I can connect to and that people can connect to as well.” What constitutes authenticity for you? Is it affective authenticity? What does authentic work look like moving forward?
NP: Authenticity looks like exploration, freedom, and truth.