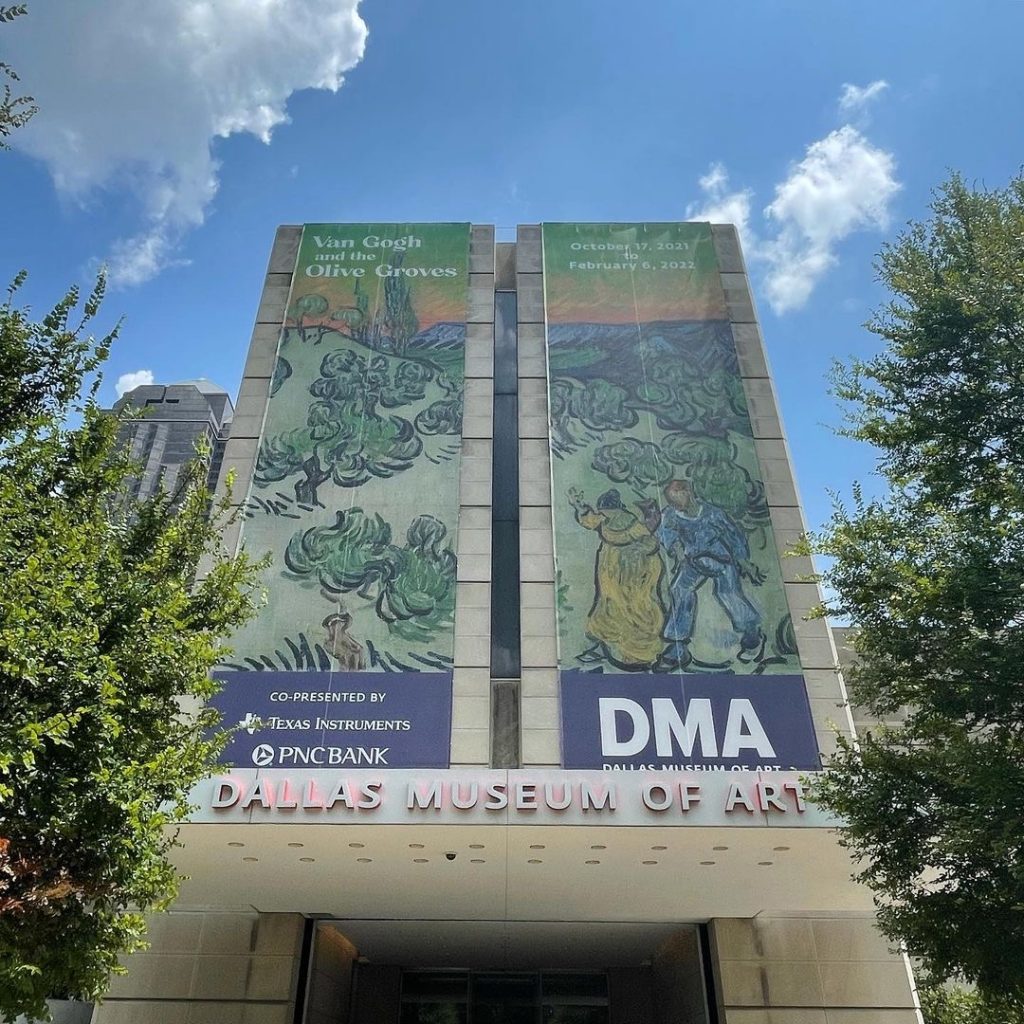
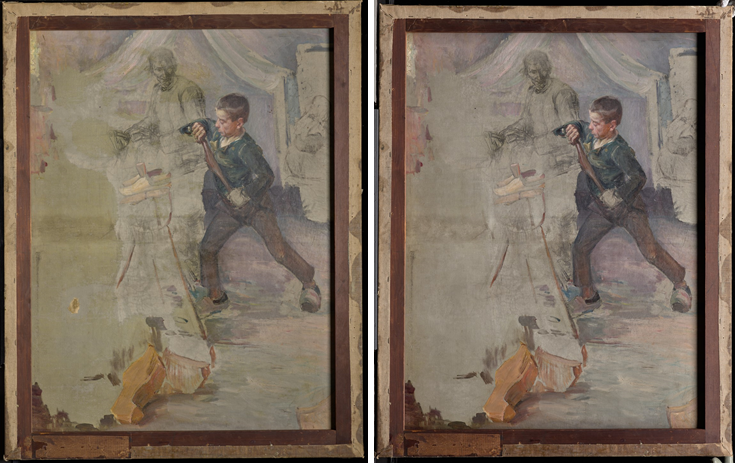Dr. Nicole R. Myers, Interim Chief Curator and The Barbara Thomas Lemmon Senior Curator of European Art, spent almost a decade working tirelessly on bringing Van Gogh and the Olive Groves to life. Read about her perspective in making the magic of the exhibition happen.
This exhibition has never been done before, and yet Van Gogh is a legendary artist. How does it feel to premiere this exhibition in Dallas?
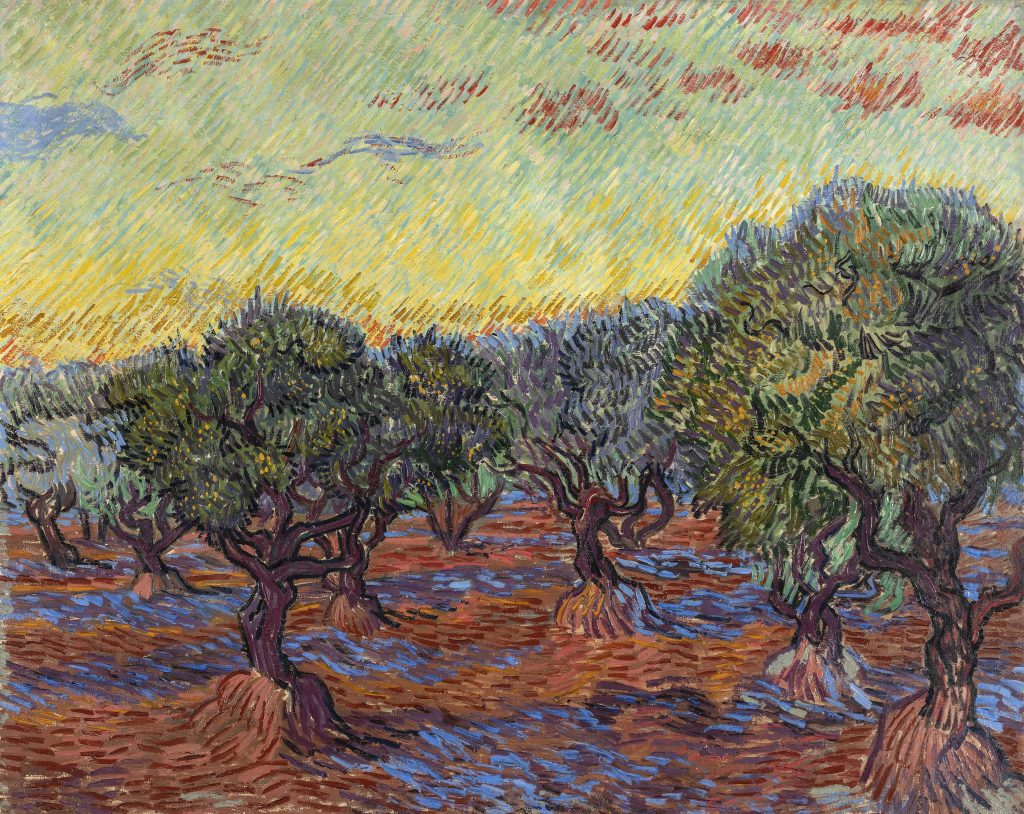
I’m incredibly excited to bring Van Gogh’s dazzling olive grove series to the DMA this fall. The paintings are not only beautiful but unique as well, and hold a special place in the artist’s life and production. Van Gogh and the Olive Groves is the very first exhibition to reunite this important, yet relatively unknown, series of paintings, and Dallas is the only place in the US to see them.
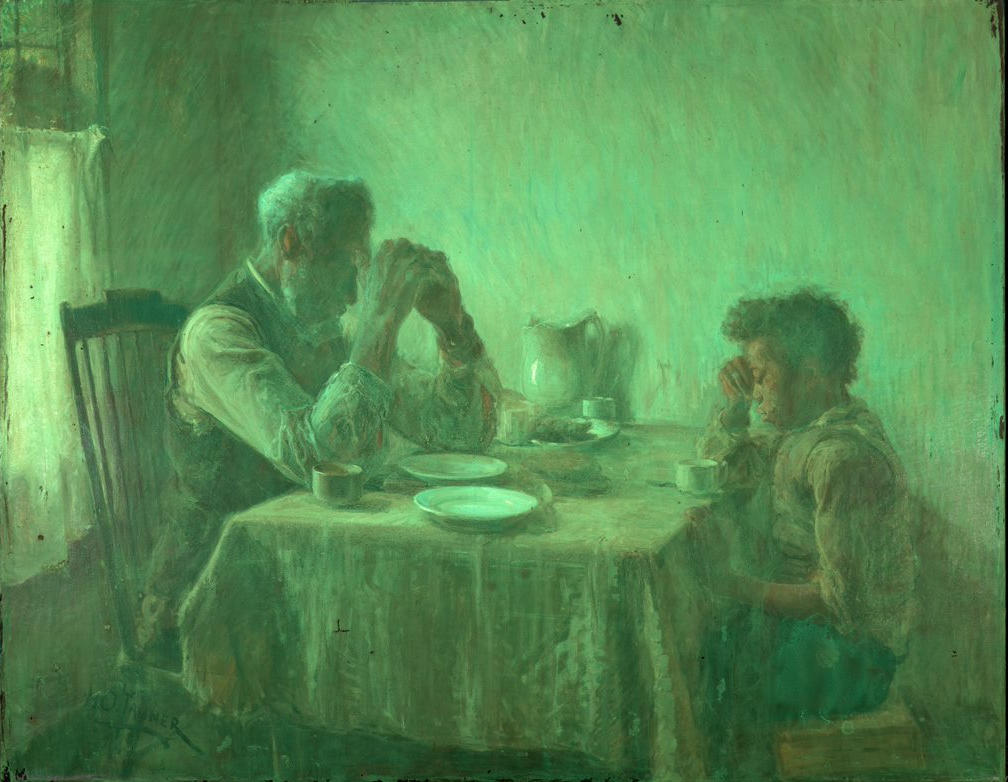
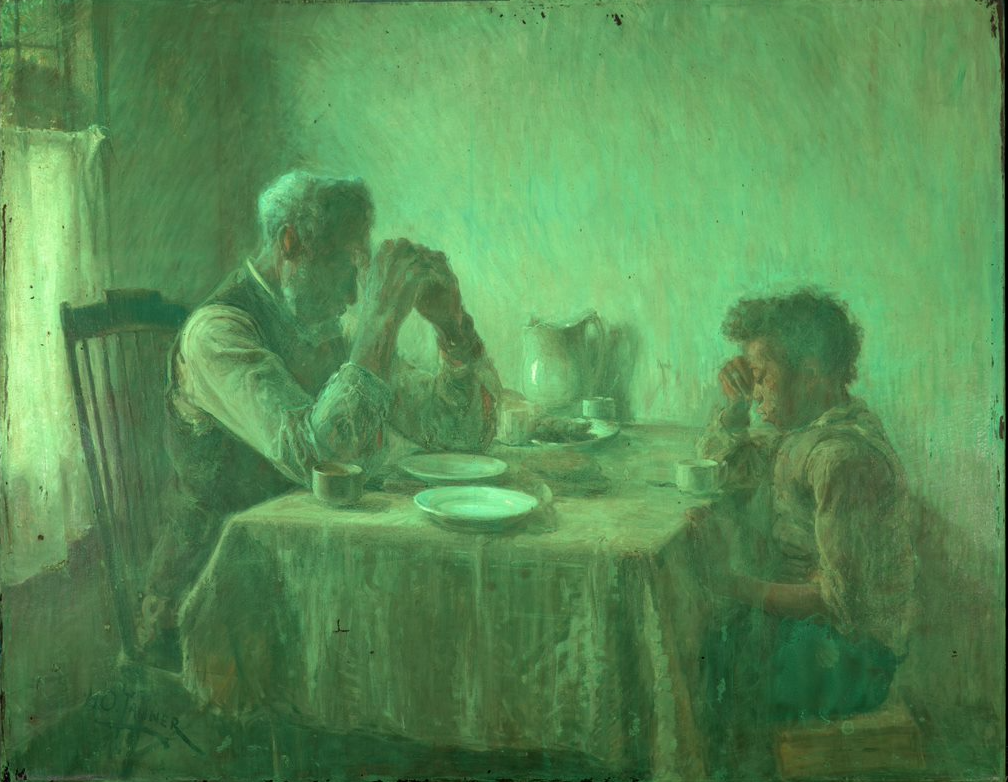
In addition to learning about Van Gogh’s olive groves—the fascinating story of their production, as well as their evolving styles and symbolism—I hope that visitors will leave with a deeper understanding and appreciation of the artist not as the mythic persona of popular culture, but as a hard-working artist and complex human being. Van Gogh painted the olive groves while he was grappling with serious mental illness at the asylum in Saint-Rémy-de-Provence. He was thoughtful and deliberate in his selection of the olive trees as a motif and the visual means he used to convey both their appearance and the deeply personal, often spiritual significance they held for him. Produced in isolation during this very difficult period of his life, the olive grove paintings were intended to provide us—the weary modern viewer—with feelings of solace, peace, and hope, something that resonates today more than ever.
What was your favorite part about working with the Van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam to make this exhibition possible?
When I first started this exhibition, I had the hope that the Van Gogh Museum (VGM) would join me on the endeavor. They have three out of the 15 paintings in the olive grove series, in addition to related drawings, so their support was tantamount to the project’s success. I initially approached my colleagues at the VGM to gauge their general interest and whether they would be willing to lend artwork to the show. Their enthusiastic response exceeded my expectations, and a wonderful partnership was born on the spot. I’m fortunate to work with such great colleagues in Dallas and Amsterdam to bring this once-in-a-lifetime show to fruition. And now, after almost a decade in the making, we’re ready to share our discoveries and passion for Van Gogh’s olive groves on both sides of the Atlantic!

How does it feel to approach the exhibition opening after so many years in development?
I began developing the concept for this exhibition in 2012, while I was researching the incredible olive tree painting by Van Gogh in the collection of the Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art in Kansas City. Although I had worked a great deal on the artist, I was shocked to find that the painting belonged to a significant series about which I knew nothing. I set out to learn more, only to find that there had been no exhibition or book dedicated to the subject to date. Moreover, there were many unknowns about the series, such as the dates of some of the paintings, the sequence in which they were made over a six-month production period, and which paintings Van Gogh was describing in his letters—something unexpected given the incredibly saturated research field dedicated to this beloved world-famous artist. With that, I launched the exhibition and the unprecedented comparative study that involved an international team of curators, researchers, conservators, and scientists.
The exhibition planning took many twists and turns along the way. It’s never easy to borrow important artwork by heavily sought-after artists such as Van Gogh, and some of our loan negotiations took five years to secure. Just as the checklist was nearly finalized, the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic brought about new challenges and uncertainties. Rather poignantly, the exhibition catalogue, which takes as its subject the artistic production of a painter confined within an asylum—an experience Van Gogh described as a “necessary and salutary quarantine”—was written and produced in its entirety during the self-isolation and confinement imposed by the pandemic. It was with a mixture of trepidation and sadness that after all these years of working tirelessly to bring this project to fruition, I didn’t have access to a library or other resources when it finally came time to start the book. But the work forged ahead and I’m deeply grateful for what we accomplished under these exceptional circumstances.
As I worked at my dining room table turned remote office, I thought often of Van Gogh and his experience at the asylum. Never before had his enduring belief in the healing and consolatory power of art and of nature felt more relevant, his experience more relatable, his achievement more astounding. I hope that visitors to the show will take as much joy and comfort from the olive trees as I have over the last decade, and especially this last year.

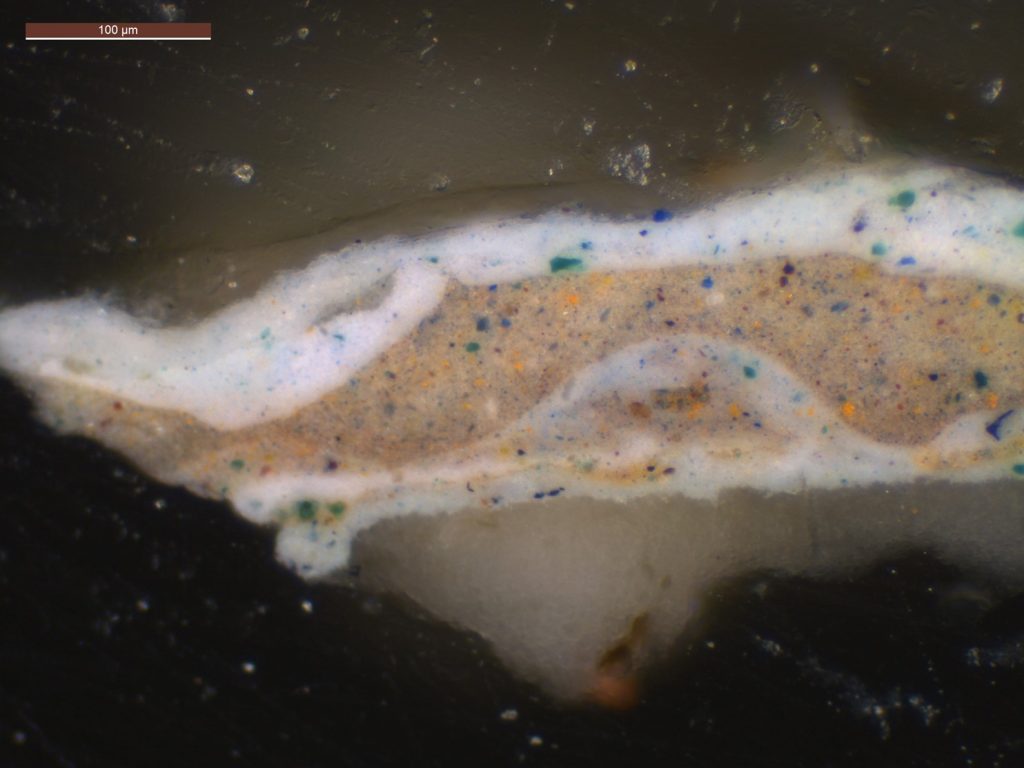
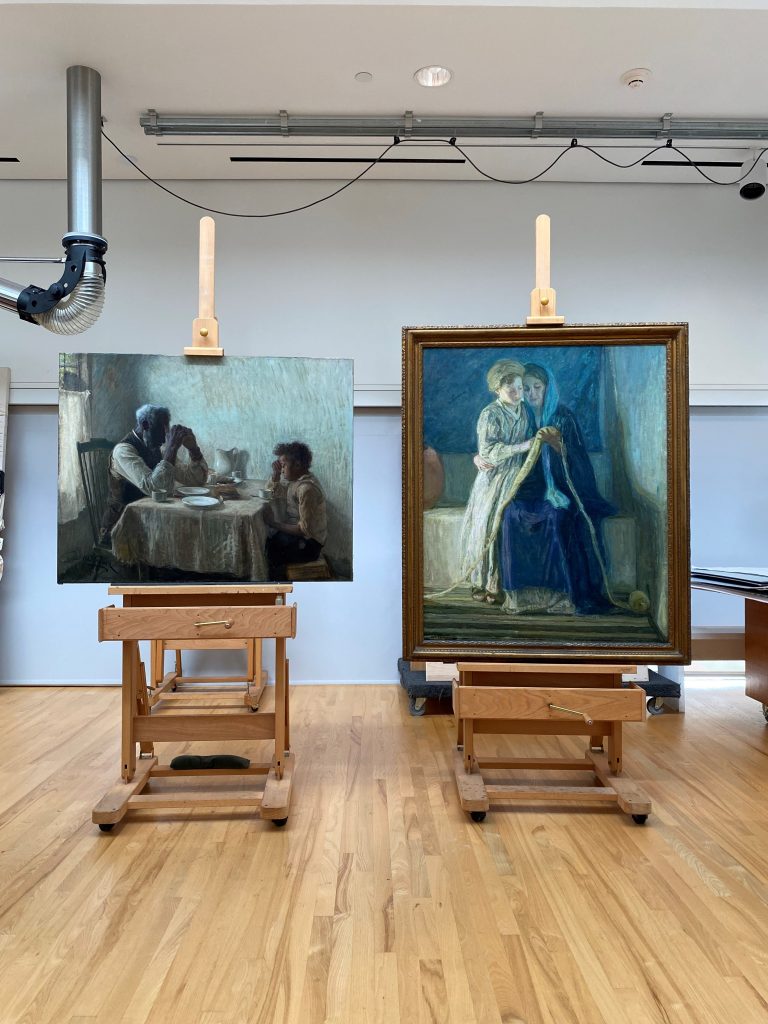
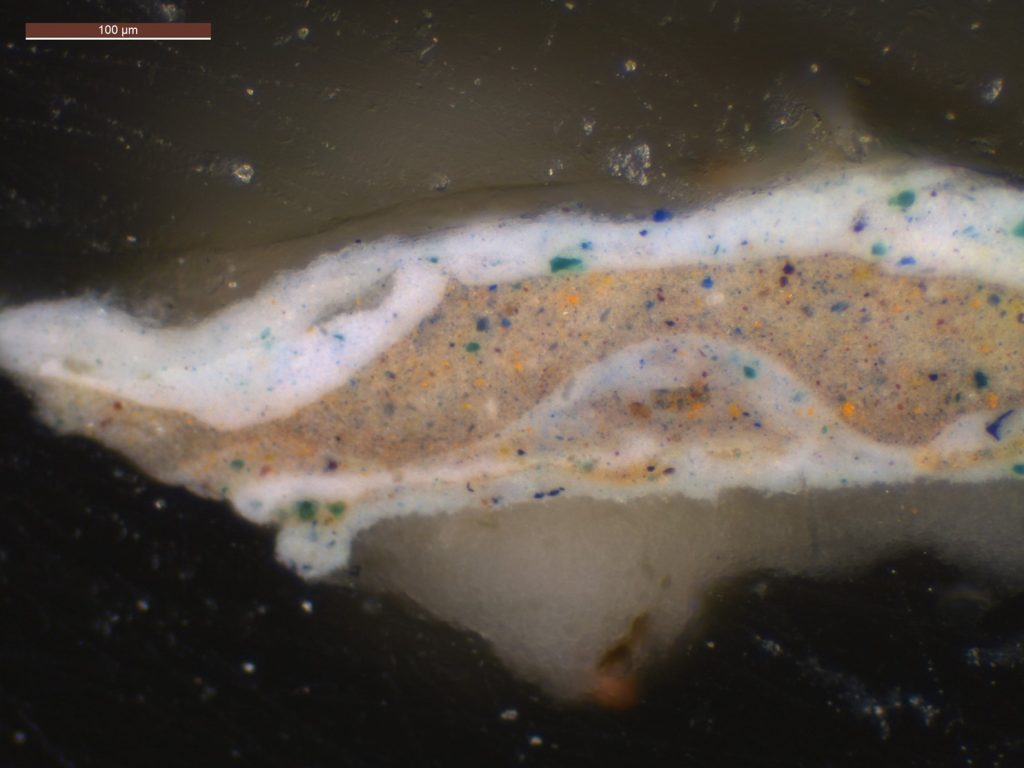
Describe some of the discoveries from the conservation study for the exhibition.
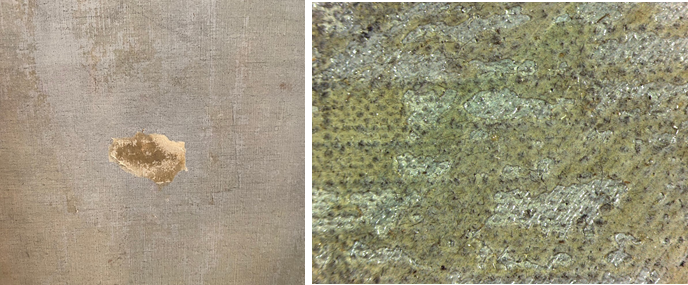
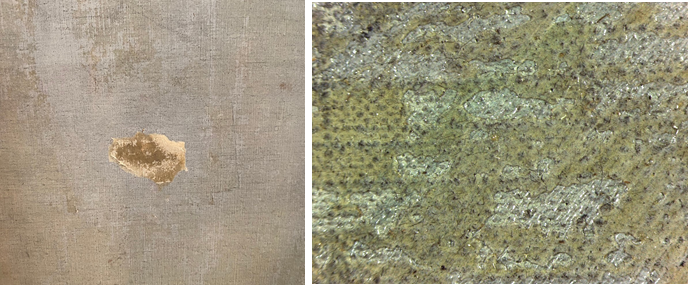
At the heart of the exhibition are the discoveries we made by studying all 15 olive grove paintings in the series. My original questions—what month did Van Gogh paint each work? In what order did he paint them? Can we connect individual paintings to specific mentions in his letters?—were explored in-depth by an international research team over the course of three years. Conservators and scientists analyzed every aspect of the olive tree paintings, from the materials used to how their appearance was altered by time. The exciting results of this three-year study make their debut in the exhibition in the chronological display of the olive groves, as well as in a dedicated gallery that will present the research team’s methods and discoveries. It’s the perfect demonstration of what’s possible when art meets science.