Because we offer free general admission, visitors often pop in for a few minutes when they are in the Dallas Arts District. Our Visitor Services team is frequently asked this question: “What would you recommend seeing if you only had thirty minutes to visit the Museum?” We thought it would be fun to pose this tough question to DMA staffers from different departments to see what they consider to be among the highlights. First up is Eric Zeidler, our Publications Manager:
If a visitor had thirty minutes and accepted me as a guide, I would take them to many galleries to highlight multiple works in the collection, starting with the African galleries on Level 3.
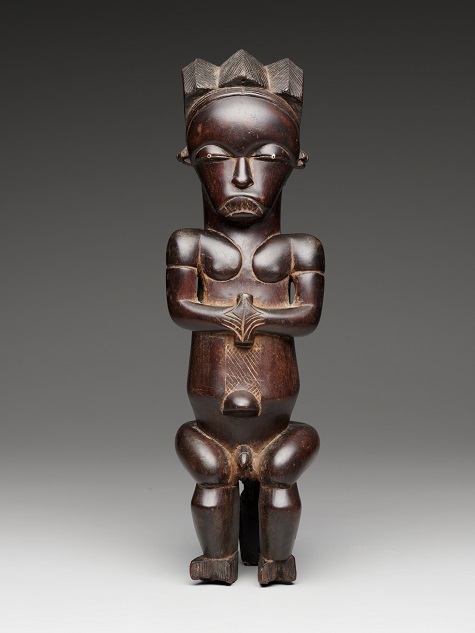
- Reliquary guardian figure (eyema-o-byeri), 1800-1860, Mvaï group, Fang peoples, Ntem region, Gabon, Africa, wood, Dallas Museum of Art, The Eugene and Margaret McDermott Art Fund, Inc.
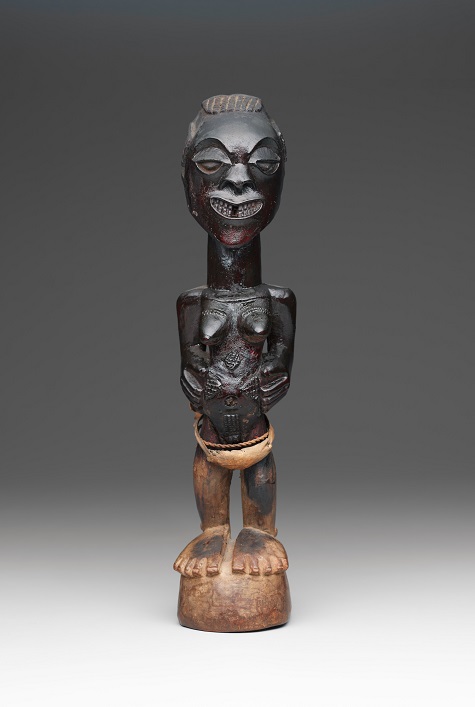
- Standing female power figure (nkishi), late 19th to early 20th century, Songye peoples, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa, wood, skin, cord, and metal, Dallas Museum of Art, The Clark and Frances Stillman Collection of Congo Sculpture, gift of Eugene and Margaret McDermott
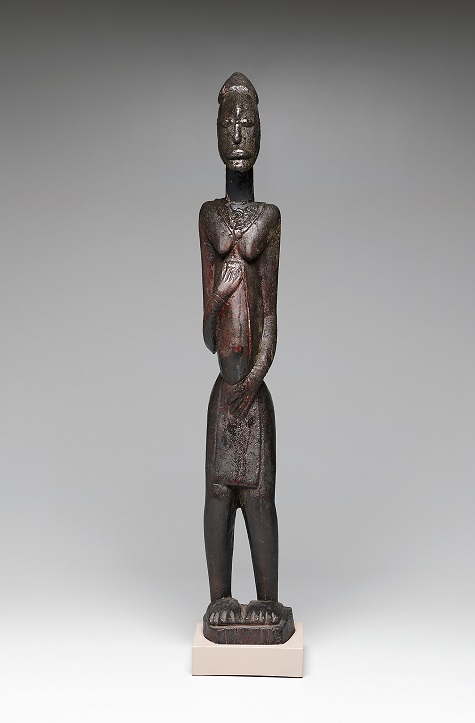
- Standing female figure, 11th–13th century, pre-Dogon culture, Djenennke/Soninke, Bandiagara Plateau, Mali, Afric, wood and oil, Dallas Museum of Art, The Gustave and Franyo Schindler Collection of African Sculpture, gift of the McDermott Foundation in honor of Eugene McDermott
My favorite stops include the Fang reliquary guardian figure. It is so riveting and perfectly carved, I can never get my fill of looking at it. Another work to visit is the Songye female power figure with her sheen (she exudes the oil with which she has been anointed down through the years) and that unnerving grin. I can well imagine her exerting a beneficent or malefic power, depending on the inner qualities of those who come into contact with her. Last stop in this gallery would have to be the Djennenke/Soninke figure, with her protuberant eyes and spare, almost angular, elegance.
- Buddha Muchalinda, late 12th-early 13th century, Khmer empire, Angkor Thom region, Cambodia, Asia, copper alloy, Dallas Museum of Art, the Cecil and Ida Green Acquisition Fund
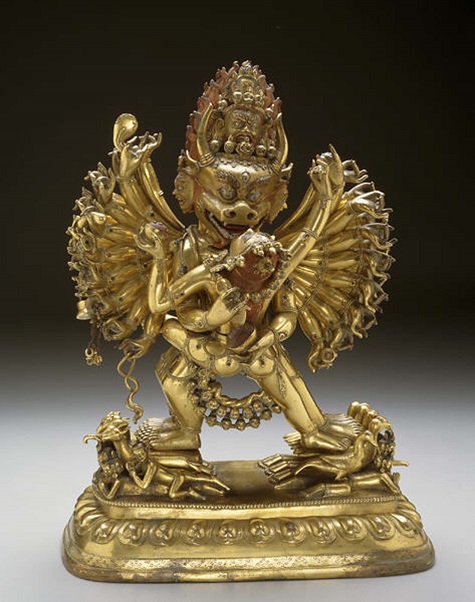
- Vajrabhairava, 18th century, Tibet, Asia, gilt bronze, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of the Alconda-Owsley Foundation to honor Dr. Anne R. Bromberg
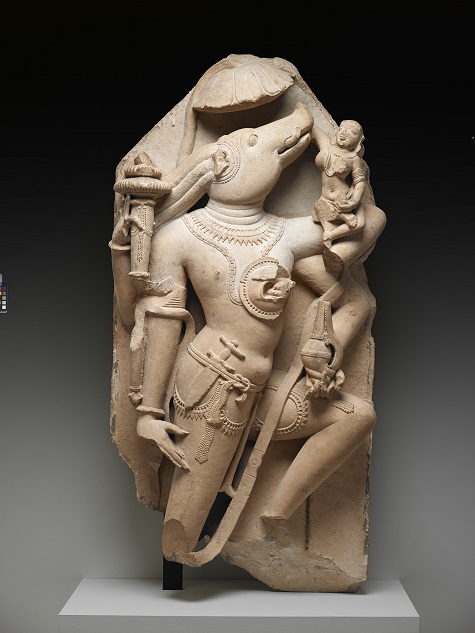
- Vishnu as Varaha, 10th century, Central, Madhya Pradesh, India, Asia, sandstone, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of David T. Owsley via the Alvin and Lucy Owsley Foundation and the Alconda-Owsley Foundation, E.E. Fogelson and Greer Garson Fogelson Fund, General Acquisitions Fund, Wendover Fund, and gift of Alta Brenner in memory of her daughter Andrea Bernice Brenner-McMullen
Continuing our tour on Level 3 in the Arts of Asia gallery includes time to take in the serene Buddha Muchalinda. I love his canopy of naga heads and the fascinating expressiveness of his lips. The Vajrabhairava, with its horns and fangs and union of ecstatic abandon with higher truth, is always a must see, as is the sensuously provocative celestial female with that scorpion on her thigh. And finally we would visit the Vishnu as Varaha, with its diagonal lines and the redoubtable tusks and snout.
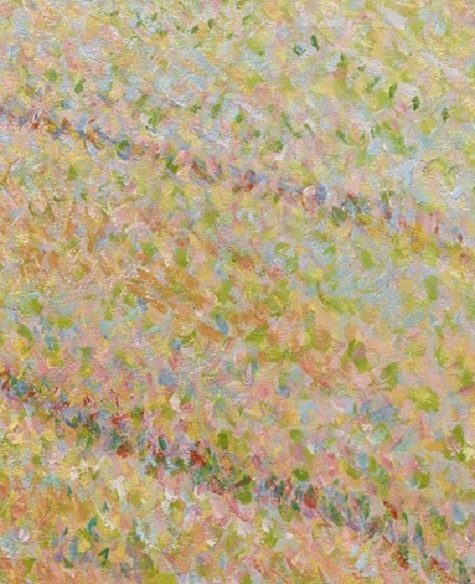
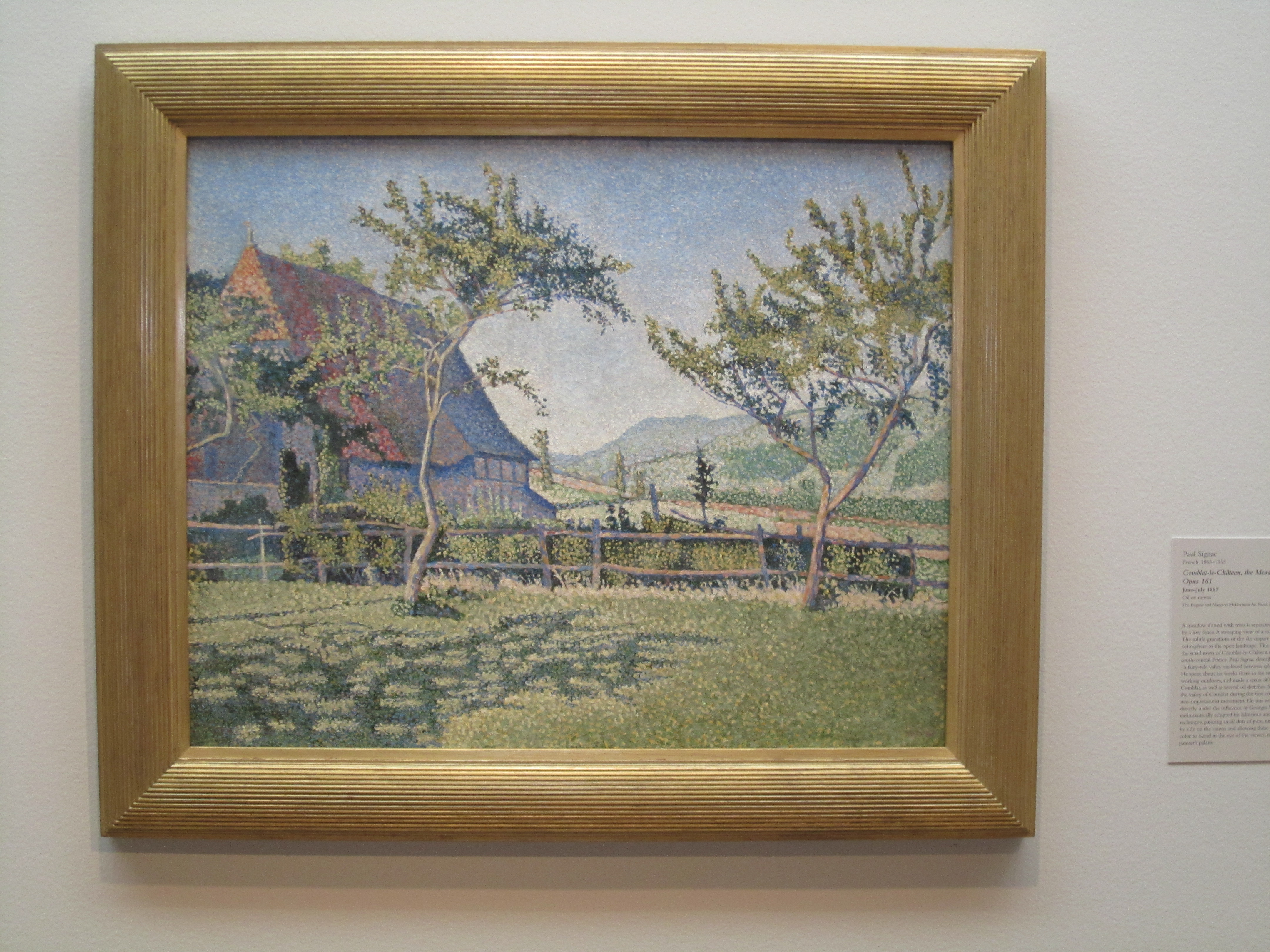
- Paul Signac, Comblat-le-Château, the Meadow (Le Pré), Opus 161, June–July 1887, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, The Eugene and Margaret McDermott Art Fund, Inc., in honor of Bonnie Pitman
- Paul Sérusier, Celtic Tale, 1894, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, Foundation for the Arts Collection, gift of Mr. and Mrs. Frederick Mayer
- Piet Mondrian. Farm Near Duivendrecht, in the Evening, c. 1916 (reprise of a compositional series from 1905 to 1908), oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of The Edward and Betty Marcus Foundation © 2012 Mondrian/Holtzman Trust c/o HCR International Washington DC
We would then dash downstairs to the European galleries on Level 2 to look at a large selection of some of my favorite works, starting with Paul Signac’s neoimpressionist masterpiece Comblat-le-Château, the Meadow (Le Pré), Opus 161. We would then continue on to Paul Sérusier’s Celtic Tale, which partly reminds me of Paul Gauguin but also has symbolist elements reminiscent of Javanese-Dutch artist Jan Toorop, with whom (for me) its imagery has luminous affinities. Next would be Piet Mondrian’s Farm Near Duivendrecht, in the Evening, with its low light, reminds me of Dahl’s Frederiksborg Castle, on view around the corner (it makes me wish that we could acquire some Atkinson Grimshaw canvases), and a quick look at Hans Hofmann’s expressive masterpiece Untitled (Yellow Table on Green).
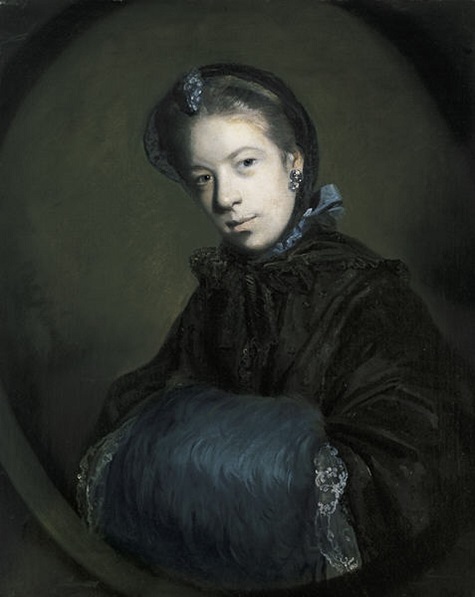
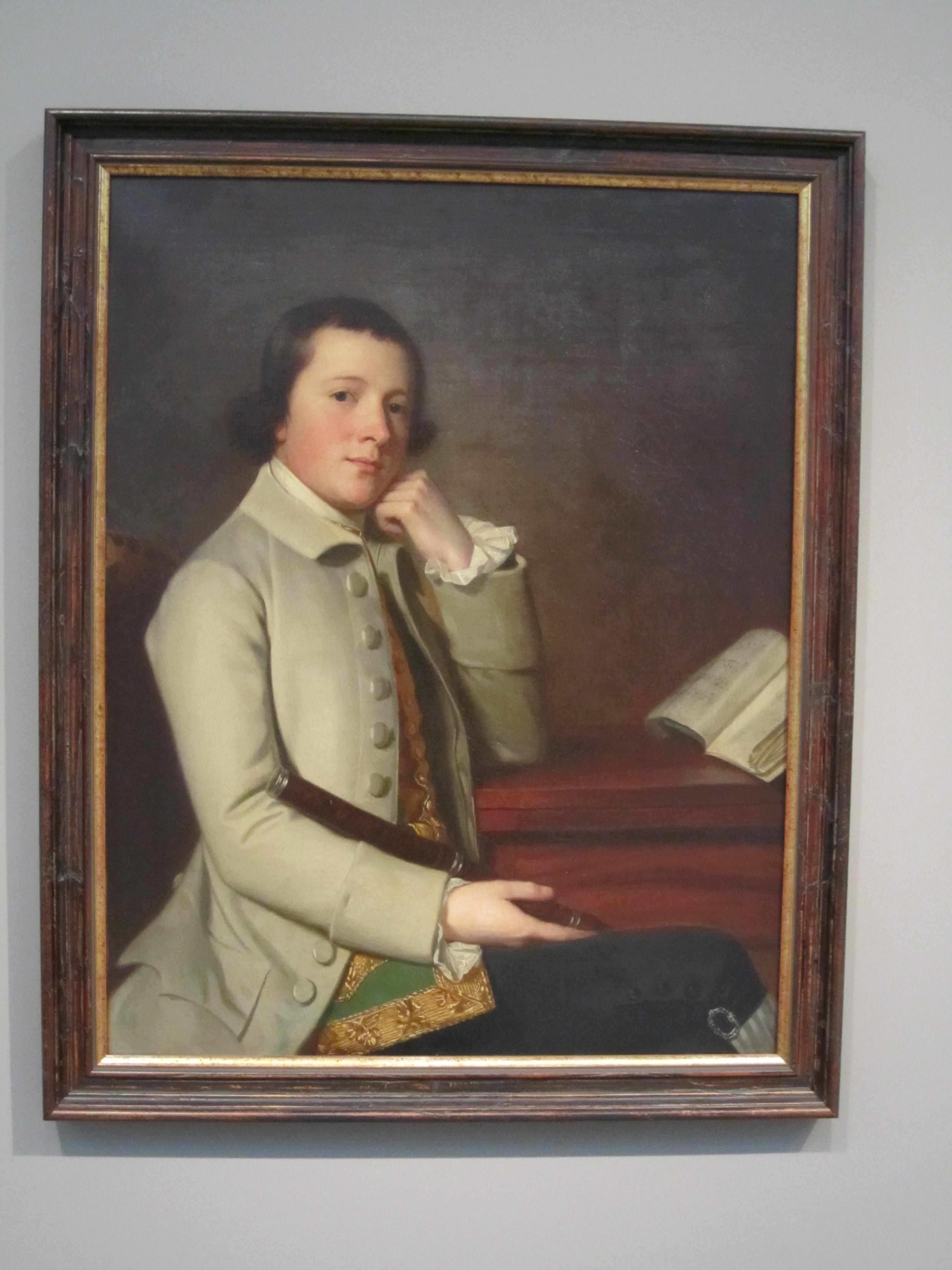
- Sir Joshua Reynolds, Portrait of Miss Mary Pelham, c. 1757, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Michael L. Rosenberg
- Cornelis Saftleven, College of Animals, 1655, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, The Karl and Esther Hoblitzelle Collection, gift of the Hoblitzelle Foundation
Going down the other side of the European galleries, I would point out the nice little Still-life with Fruit by Emilie Preyer; Sir Joshua Reynolds’ commanding Portrait of Miss Mary Pelham (she has such a penetrating stare, which for me suggests a certain formidable willfulness); the gorgeous still-life Basket of Flowers by Beert the Elder, with its petals lying strewn on a tabletop; and my beloved College of Animals by Cornelis Saftleven. I think this work, beyond its allegorical subtleties and its charm for all those who love animals, is a beautifully painted canvas, and I love studying its various striking details.
- Eye-dazzler blanket, c. 1880-1900, Navajo, Arizona, United States, North America, cotton (warp) and wool (weft, Germantown commercial wool yarn), Dallas Museum of Art, Textile Purchase Fund
- Roberto (Nervo) Montenegro, The Shell, c. 1936, oil on composition board, Dallas Museum of Art, Dallas Art Association Purchase
I would also take a quick trip to the Level 4 to see the Dust Bowl and other Texas paintings, which show that beauty can be found amidst stark desolation, and the Navajo eye-dazzler blanket, which is a pleasure to gaze upon. We would end our whirlwind tour with the fascinating little painting by Roberto Montenegro, The Shell, one of my favorite works in the entire collection.
Follow Uncrated to catch the next DMA Dash and more behind-the-scenes scoops. Visit our collection online anytime here.
Reagan Duplisea is the Associate Registrar, Exhibitions at the DMA.