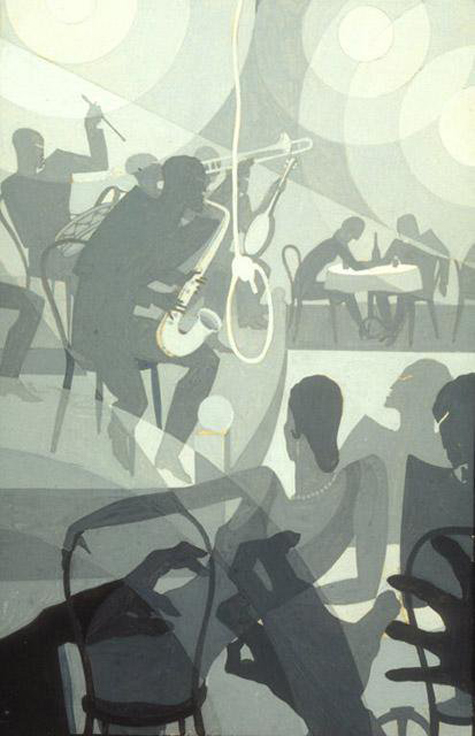April celebrates one of the most joyous and “most American” music styles—jazz. In fact, jazz is such an important part of American culture that a whole decade in American history, the 1920s, has come to be known as the Jazz Age. In the DMA spaces, you can find connections between the visual arts and jazz every week on Thursday evenings from 6:00 to 8:00 p.m. during Jazz in the Atrium.
In our newest exhibition, Youth and Beauty: Art of the American Twenties, you can see the work of jazz admirer and Harlem Renaissance leader Aaron Douglas. In Charleston (which references Paul Morand’s novel Black Magic), Douglas depicts the jazz scene set within the African community, in which the genre has part of its roots. Commenting on a later work, Douglas equated the figures in the painting with different types of music, describing the saxophone player as a representation of jazz and “Songs of Joy and the Dance.”
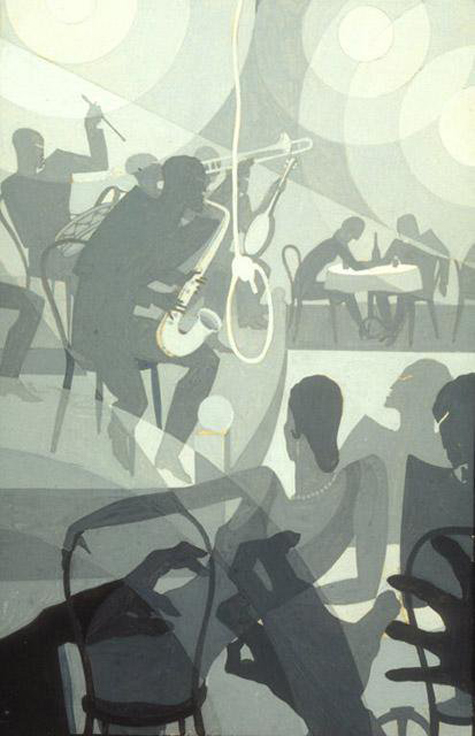
Aaron Douglas, "Charleston," c. 1928, gouache and pencil on paper board, North Carolina Museum of Art
Douglas’s contemporary and fellow jazz enthusiast Stuart Davis is featured in the American galleries with a work that, although subtly, also reveals the rhythms of the Jazz Age. Not only do the bold colors and forms of Electric Blub reflect the energy of the time, but the subject speaks to the modernism and industrialization of 1920s America.
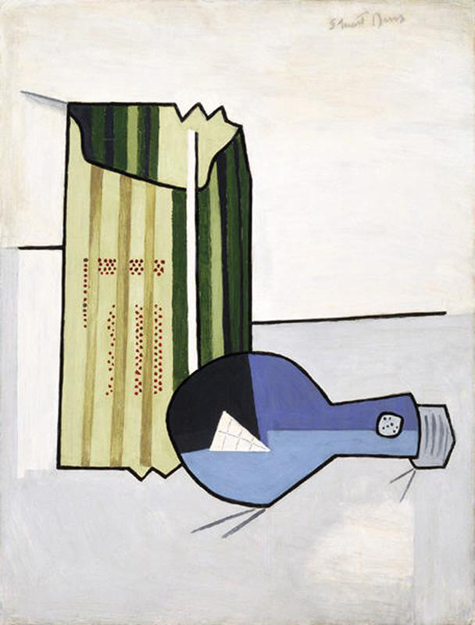

Stuart Davis, "Electric Bulb," 1924, oil on board, Dallas Museum of Art, Fine Arts Collectible Fund, 1988.59, © Estate of Stuart Davis / Licensed by VAGA, New York, NY
Nearby, a stunning portrait sculpture of the jazz musician Huddy “Leadbelly” Ledbetter serves as an appropriate transition in our jazz-inspired tour between Davis’s painting and William Waldo Dodge’s Skyscraper cocktail shaker with cups. Developing rapidly in the 1920s, the skyscraper became, together with jazz, a symbol of a free, modern America, inspiring designers across the country.

Michael G. Owen, Jr., "Leadbelly," 1943, black serpentine, Dallas Museum of Art, Mr. and Mrs. Tom Gooch Fund Purchase Prize, Twelfth Annual Texas Painting and Sculpture, 1950-1951, 1950.91
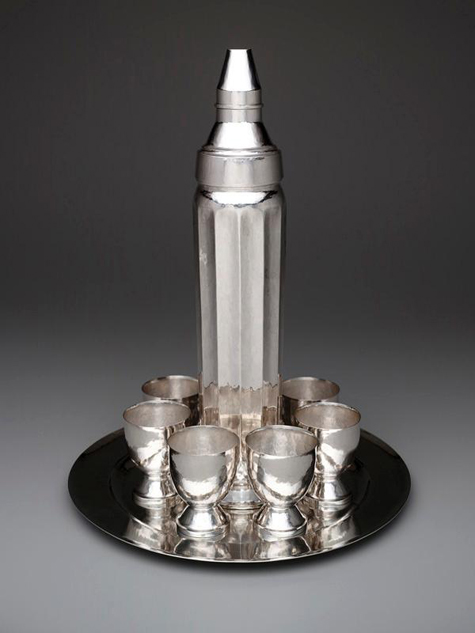

William Waldo Dodge, Jr., “Skyscraper” cocktail shaker with cups, c. 1928-1931, silver, Dallas Museum of Art, The Patsy Lacy Griffith Collection, gift of Patsy Lacy Griffith by exchange, 2008.48.1-12
But if the connections we’ve made so far are too obvious or the works too representational for your taste, don’t worry; make your way toLevel 3, where you will find works by abstract artists and jazz lovers Jackson Pollock and Piet Mondrian.
With improvisation being a key feature of jazz music, some argue that the process in this genre is at least as important as (perhaps more than) the end result. The same can be said of Pollock’s and Mondrian’s work. Pollock moving around his canvas as he pours the paint can be compared to a jazz musician improvising during a performance; both represent similar artistic expressions and ultimate celebrations of their respective arts.

Jackson Pollock, Cathedral, 1947, enamel and aluminum paint on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Mr. and Mrs. Bernard J. Reis, 1950.87 © Pollock-Krasner Foundation / Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York

Piet Mondrian, "Place de la Concorde," 1938-1943, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, Foundation for the Arts Collection, gift of the James H. and Lillian Clark Foundation, 1982.22.FA © 2012 Mondrian/Holtzman Trust c/o HCR International Washington DC
A big fan of boogie-woogie and a seeker of balance and equilibrium, Mondrian used his intuition to place and arrange the lines in works such as Place de la Concorde—much like a jazz musician would intuitively improvise on his instrument. In fact, Mondrian identified with jazz and boogie-woogie so much that he once said:
“True boogie woogie I conceive as homogeneous in intention with mine in painting: destruction of melody, which is the equivalent of destruction of natural appearance, and construction through the continuous opposition of pure means—dynamic rhythm.”
As you can see, jazz can be a treat not only for your ears but also for your eyes! So come celebrate Jazz Appreciation Month any (or every) Thursday night in April at the DMA!
Vivian Barclay is the McDermott Graduate Curatorial Intern for Decorative Arts and Design at the Dallas Museum of Art.
Mary Jordan is the McDermott Education Intern for Family Experiences and Access Programs at the Dallas Museum of Art.