Uncrated recently took a “field trip” to Fort Worth to visit the Kimbell Art Museum’s presentation of Picasso and Braque: The Cubist Experiment, 1910–1912, for which the DMA loaned its 1912 Braque painting Still Life with Bottles and Glasses. Before the exhibition opened, the Kimbell’s director of conservation, Claire Barry, took a look at our “gem of a painting” and offered us this guest post on the experience.

Georges Braque, "Still Life with Bottles and Glasses", 1912, oil on canvas, Dallas Museum of Art, The Eugene and Margaret McDermott Art Fund, Inc., given in honor of Deedie Rose and J. E. R. Chilton
I was delighted to have the opportunity to examine Braque’s Still Life with Bottles and Glasses from the DMA in the Kimbell conservation studio. Fortunately, this gem of a painting is unlined, which is rare for a cubist painting from this period. As a result, the impastoed (thickly textured) surface has never been flattened through lining. As one of my teachers wisely advised, think about a painting as a sculpture in low relief. If you look at the Braque in this way, you quickly begin to appreciate the rich variety in the artist’s application of paint—from thin areas where the paint is more fluid to thicker areas of impasto where he applied paint with a heavily loaded brush. Then, in the upper left, you might notice that the paint has a crusty texture that seems totally unrelated to the composition. With the permission of the DMA curators, I x-rayed the painting, which quickly revealed that Braque completely reworked the composition of Still Life with Bottles and Glasses during the course of painting. The texture of the underlying paint layers, later covered over, can still be seen on the surface. I was fascinated to discover this, because between Picasso and Braque, I always believed that Picasso had a greater tendency to radically rework his paintings (as he did with the Kimbell’s Man with a Pipe). Braque painted the Kimbell’s Girl with a Cross without making a single revision.
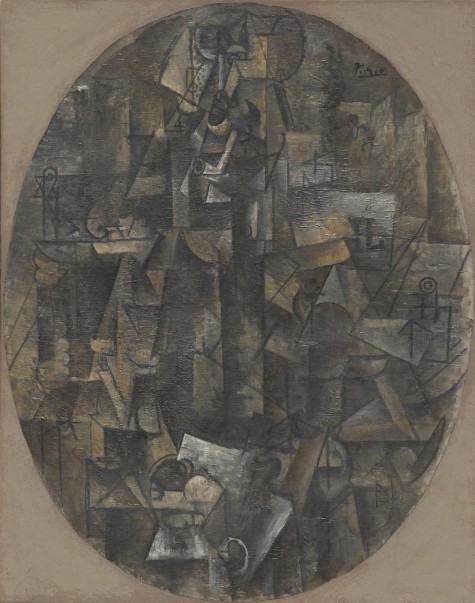

Pablo Picasso, Man with a Pipe, 1911, oil on canvas, Kimbell Art Museum. Photo © MegaVision. © 2011 Estate of Pablo Picasso / Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York
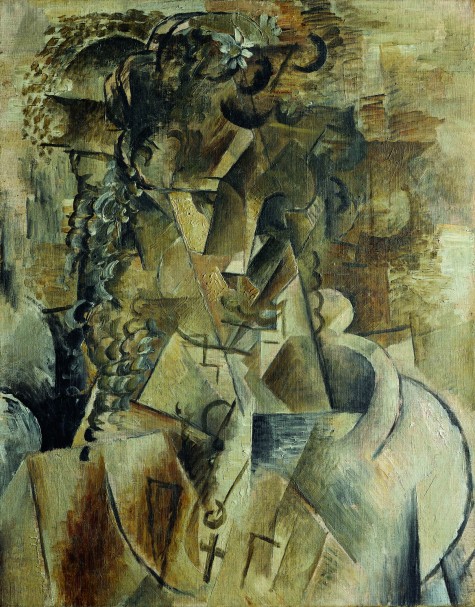
Georges Braque, Girl with a Cross, 1911, oil on canvas, Kimbell Art Museum. Photo © MegaVision. © 2011 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris
I was fortunate to be able to examine the two Braques, the DMA’s and the Kimbell’s, side by side in the conservation studio. Like the DMA painting, the Kimbell’s Girl with a Cross is unlined and preserved in pristine condition. In fact, it has never been varnished and retains the matte surface that the cubists intended. Both Picasso and Braque were adamant that their paintings should never be varnished. The DMA’s Braque, however, had been varnished at some point, and the varnish layer imparted a glossier surface than Braque had in mind. The unifying effect of the varnish also masked the subtle differences in surface gloss and texture that Braque created. In preparation for the exhibition, the DMA gave me permission to remove the varnish layer from Still Life with Bottles and Glasses. The fact that visitors to the exhibition can now see two unlined, unvarnished cubist paintings by Braque is really something exceptional. When you see the surfaces of these paintings, you can feel confident that this is very close to how they appeared when they left Braque’s easel some one hundred years ago.
Braque’s Still Life with Bottles and Glasses (1912) was sent to the Kimbell for spectral-image photography during the early stages of planning the exhibition Picasso and Braque: The Cubist Experiment, 1910–1912. These photographs are among the many incredible high-resolution digital images that can be explored with the iPad application iCubist in the Kimbell exhibition. If you want to experience the details in cubist paintings, brushstroke for brushstroke (the way I examine paintings in my job as a paintings conservator), I really recommend that you check out the iPads at the Kimbell. To my knowledge, this is the first time such images have been made available to the public in such an interactive way in a museum exhibition. The goal is to enrich the experience of seeing the real paintings, for which there is absolutely no substitute. My hope is that the iPad application may encourage visitors to spend even more time in the exhibition. Unlike the Acoustiguide, you cannot look at a painting and the iPad app simultaneously. So perhaps this will encourage visitors to look at the paintings first, then explore the iPad, and then return to the paintings for a second look, with greater understanding and appreciation.
Guest blogger Claire Barry is the director of conservation at the Kimbell Art Museum.








![Badu Concert Crowd[1]](http://blog.dma.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/badu-concert-crowd1-e1307382070251.jpg)





![photo[8]](http://blog.dma.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/photo8-e1306966221312.jpg)
![photo[7]](http://blog.dma.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/photo7-e1306966274528.jpg)
![photo[6]](http://blog.dma.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/photo6-e1306966300541.jpg)
![photo[5]](http://blog.dma.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/photo5-e1306966324187.jpg)
![photo[2]](http://blog.dma.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/photo2.jpg)
![photo[3]](http://blog.dma.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/photo3-e1306966441820.jpg)









