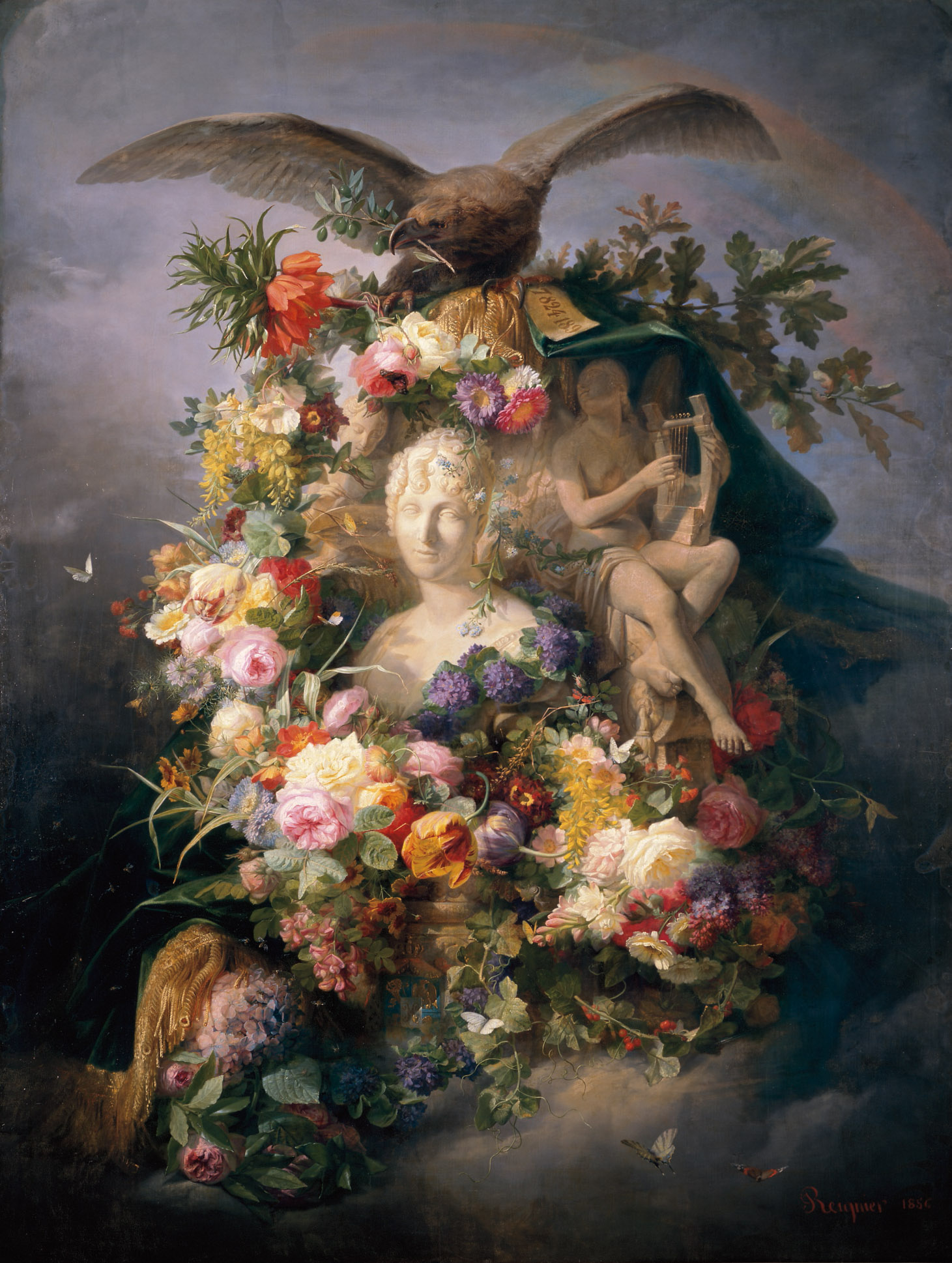
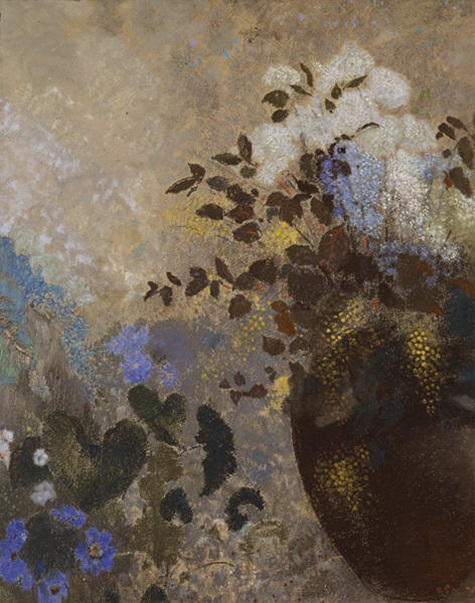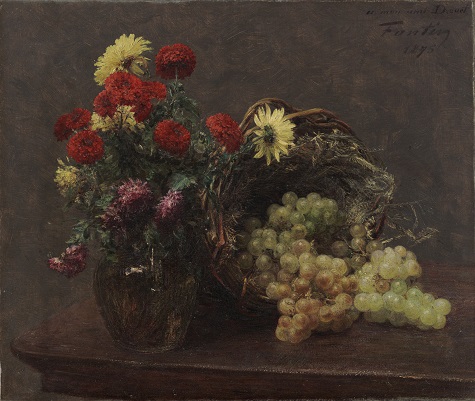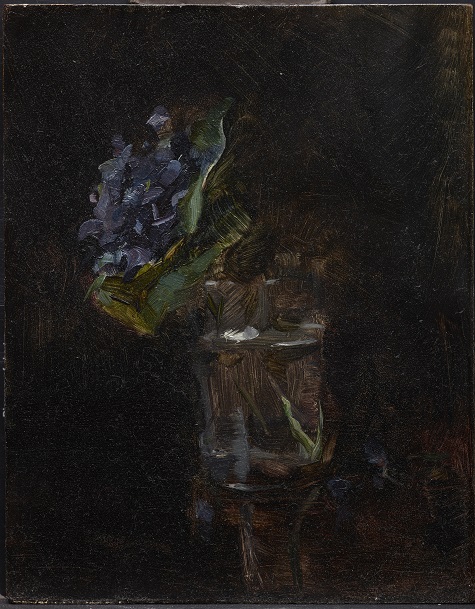With Bouquets: French Still-Life Painting from Chardin to Matisse closing this weekend, you only have a few days left to enjoy the blossoming canvases in the exhibition. The tradition of recreating bundles of blooms in art as still-life is longstanding. Many of the floral arrangements you’ll see are bright, plush tableaus with numerous species represented. They demonstrate the prowess of French master artists who nestled cultural symbols throughout the canvas.
In contrast, neither silk ribbon nor glittering vase contain the artworks celebrating iconic Texas flora from the Museum’s permanent collection. They are rendered on paper or hardboard in print or with brush. Realistically portrayed in muted tones, a single species is the subject of each work. These plants thrive in the unique climate of our rugged state and have been cultivated by humans for centuries for medicine, sustenance and beauty.
- Merritt Mauzey, Cotton Stalk, n.d., Dallas Museum of Art, gift of W.A. Brooks, Jr.
- Florence E. McClung, Castor Beans, n.d., Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Florence E. McClung.
Merritt Mauzey’s print Cotton Stalk and Florence McClung’s print Castor Beans resemble naturalist studies from early botanical books. The plants are highly detailed and placed against a void background to isolate their physical attributes. You can also see similarities to Art Nouveau motifs in Mauzey’s print. The cotton stalks are frontal and flattened with sinuous stems. Cotton has been a leading cash crop in Texas for generations. Every part of the plant can be put to use, especially the tuft of fibers which is removed and spun into thread. Castor-beans, on the other hand, have highly toxic seeds containing ricin and are hazardous to most livestock.
- Otis Dozier, Cotton Boll, 1936, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of Eleanor and C. Thomas May, Jr.
- Otis Dozier, Maize and Windmill, 1937, Dallas Museum of Art, The Barrett Collection.
Otis Dozier, on the other hand, places Texas staple crops in a portrait style composition with their respective farm settings as the backdrop. In Cotton Boll, Dozier depicts the sequence of growth as we are reminded that flora has a brief but bountiful life cycle. Some art scholars believe Maize and Windmill resembles millet as the size and shape of the plant look somewhat like Red Millet or Sorghum. Maize has been cultivated and prepared as food in numerous ways since ancient times in North America. The shape or color of the seeds can be an indicator of their diverse genes.

Charles T. Bowling, Meadow Wind, 1942, Dallas Museum of Art, Ted Dealey Purchase Prize, Fourteenth Annual Dallas Allied Arts Exhibition, 1943.
Sunflowers have long been used by indigenous North Americans for many reasons, like treating snake bites or making oils. In some parts of Texas they can grow up to eight feet tall, with flower heads one foot in diameter! Charles T. Bowling captures the strength of the sunflower in its natural setting in his watercolor Meadow Wind.
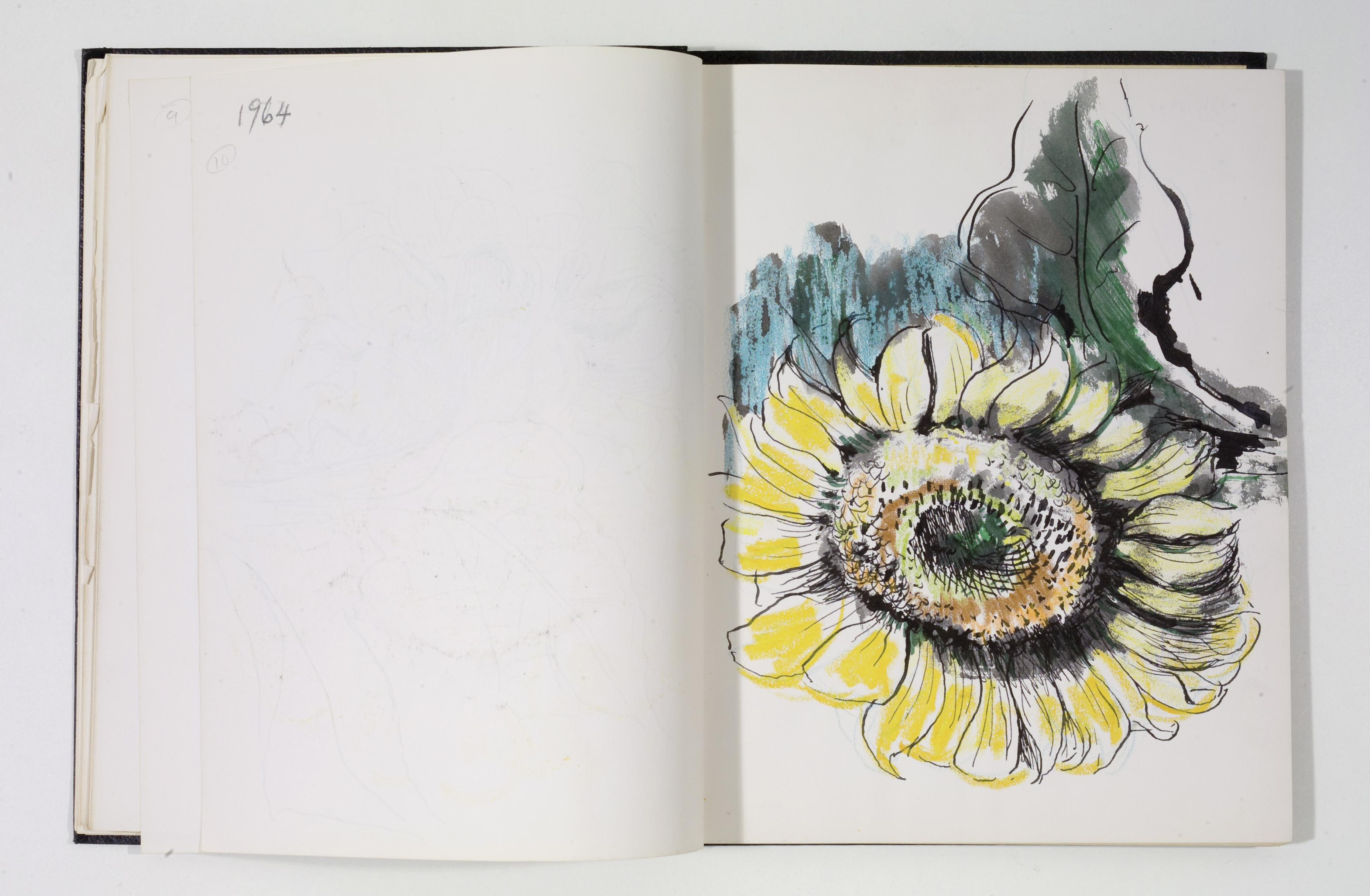
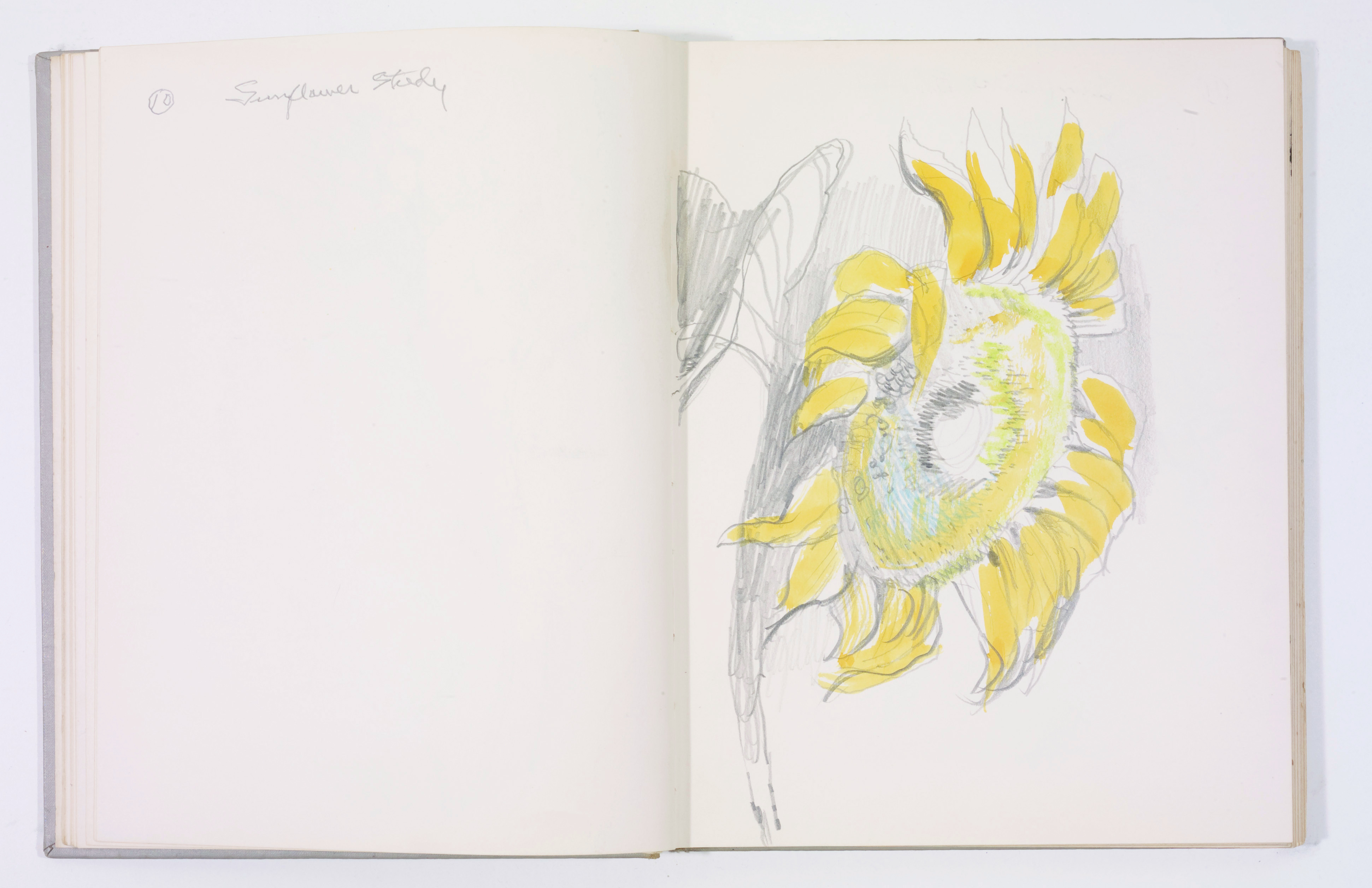
- Otis Dozier, Sketchbook, 1964-1965, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of The Dozier Foundation.
- Otis Dozier, Sketchbook, 1963-1978, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of The Dozier Foundation.
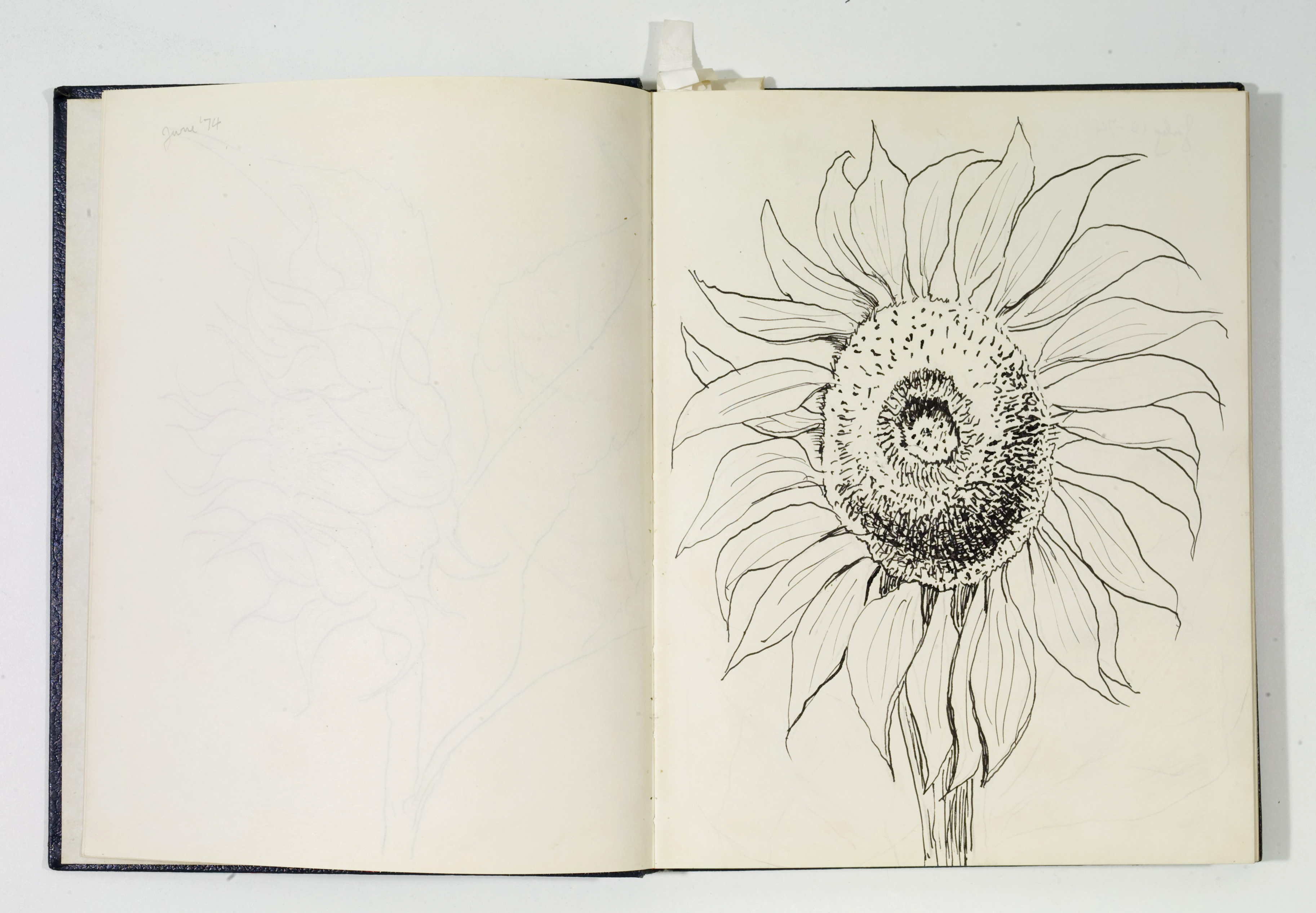
- Otis Dozier, Sketchbook, 1974, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of The Dozier Foundation.
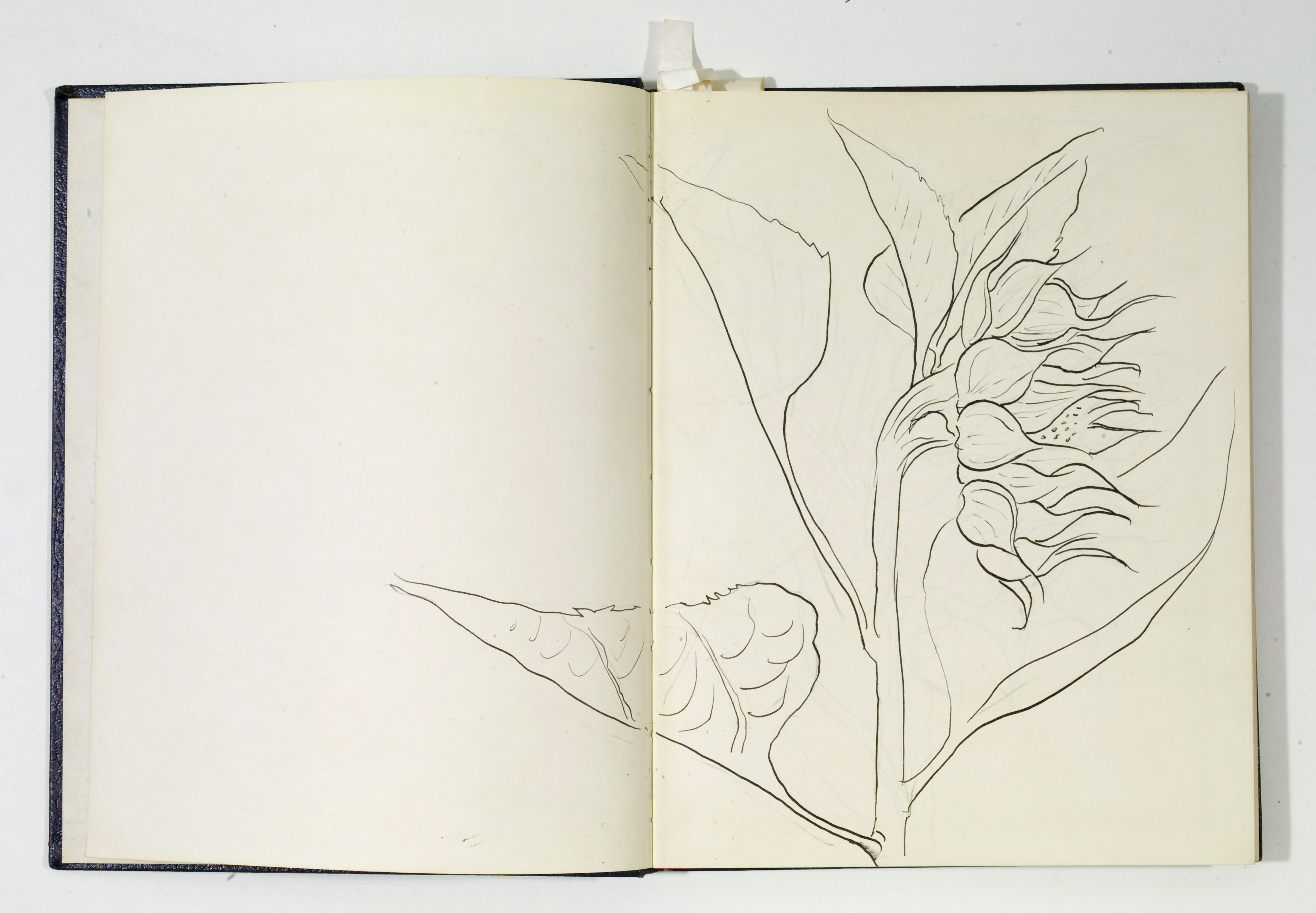
- Otis Dozier, Sketchbook, 1974, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of The Dozier Foundation.
Throughout the pages of many sketchbooks by Otis Dozier are studies of sunflower heads. It is interesting to see an artist working through his observations of nature. He uses the blank pages to examine the texture and form of the sunflower at various angles.
Imagine all the unique decorative arrangements that could be made with the regional flora of Texas. And there are many other examples of Texas flora in the collection to explore. Try searching for ‘jimson weed,’ ‘coxcomb,’ or ‘cactus’ in the DMA’s online collection database. And when you stop by for your last peek at Bouquets, see what other blooms you can find in our galleries!
Rae Pleasant
Research Associate for Early Texas Art