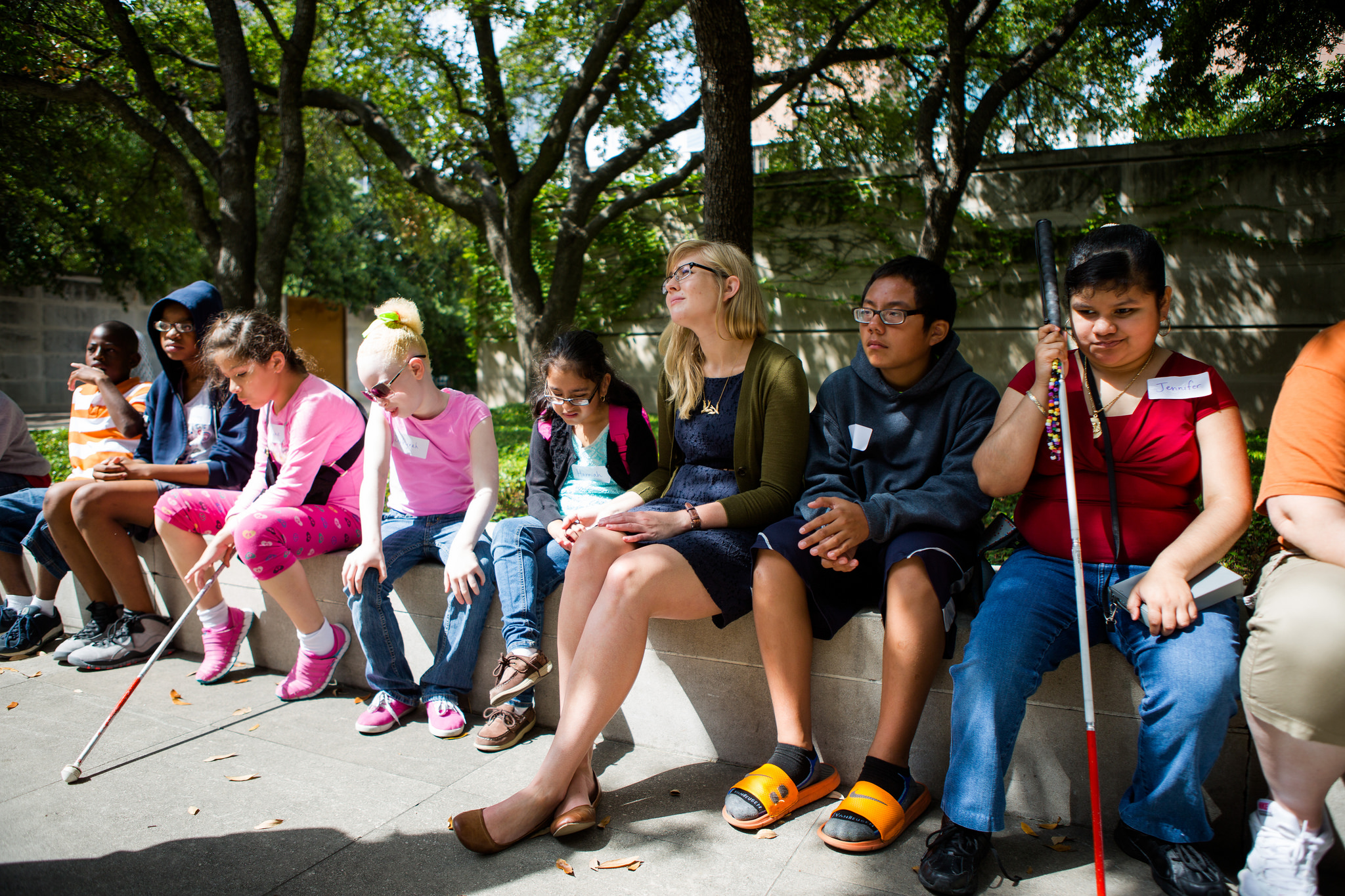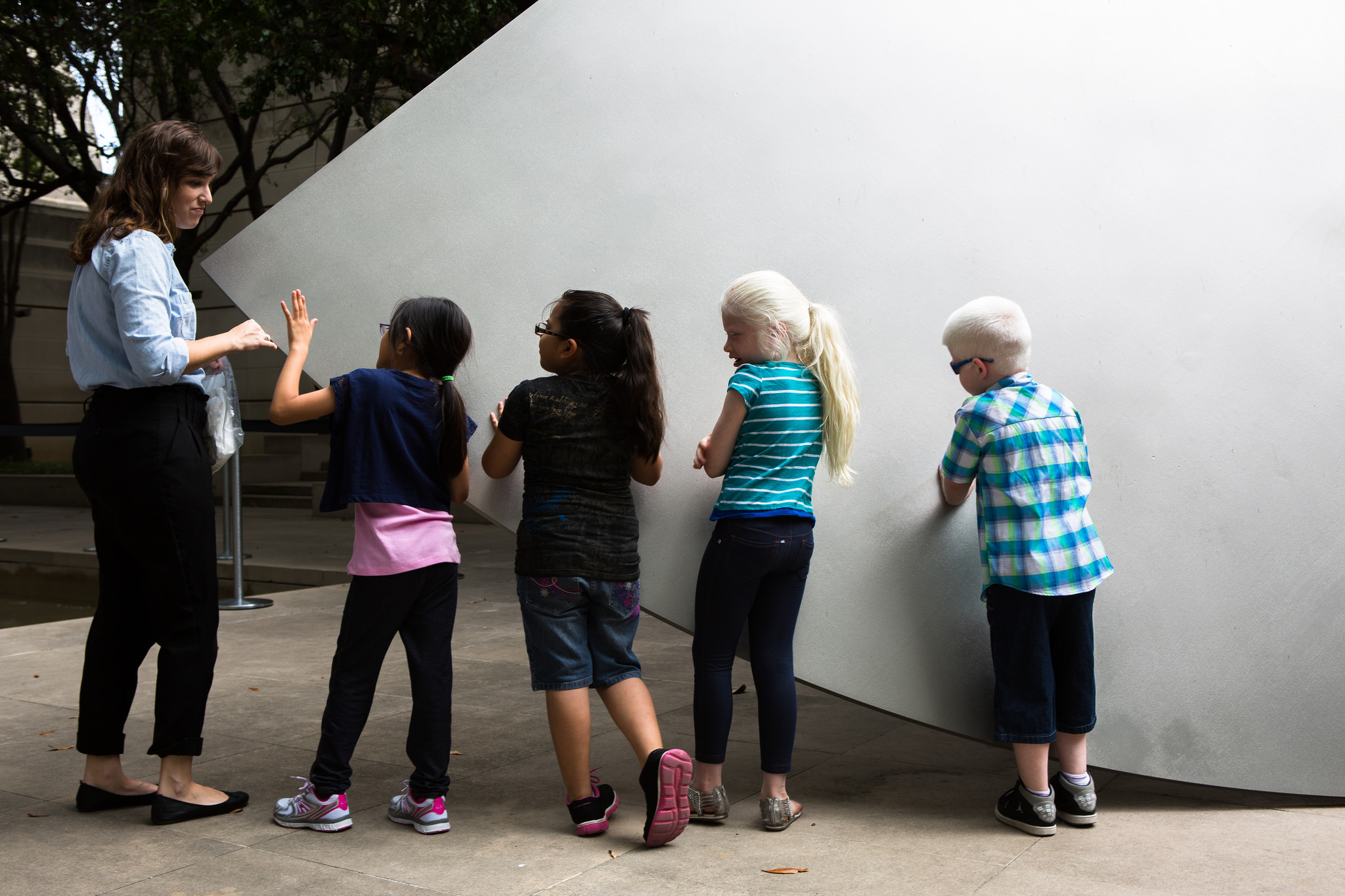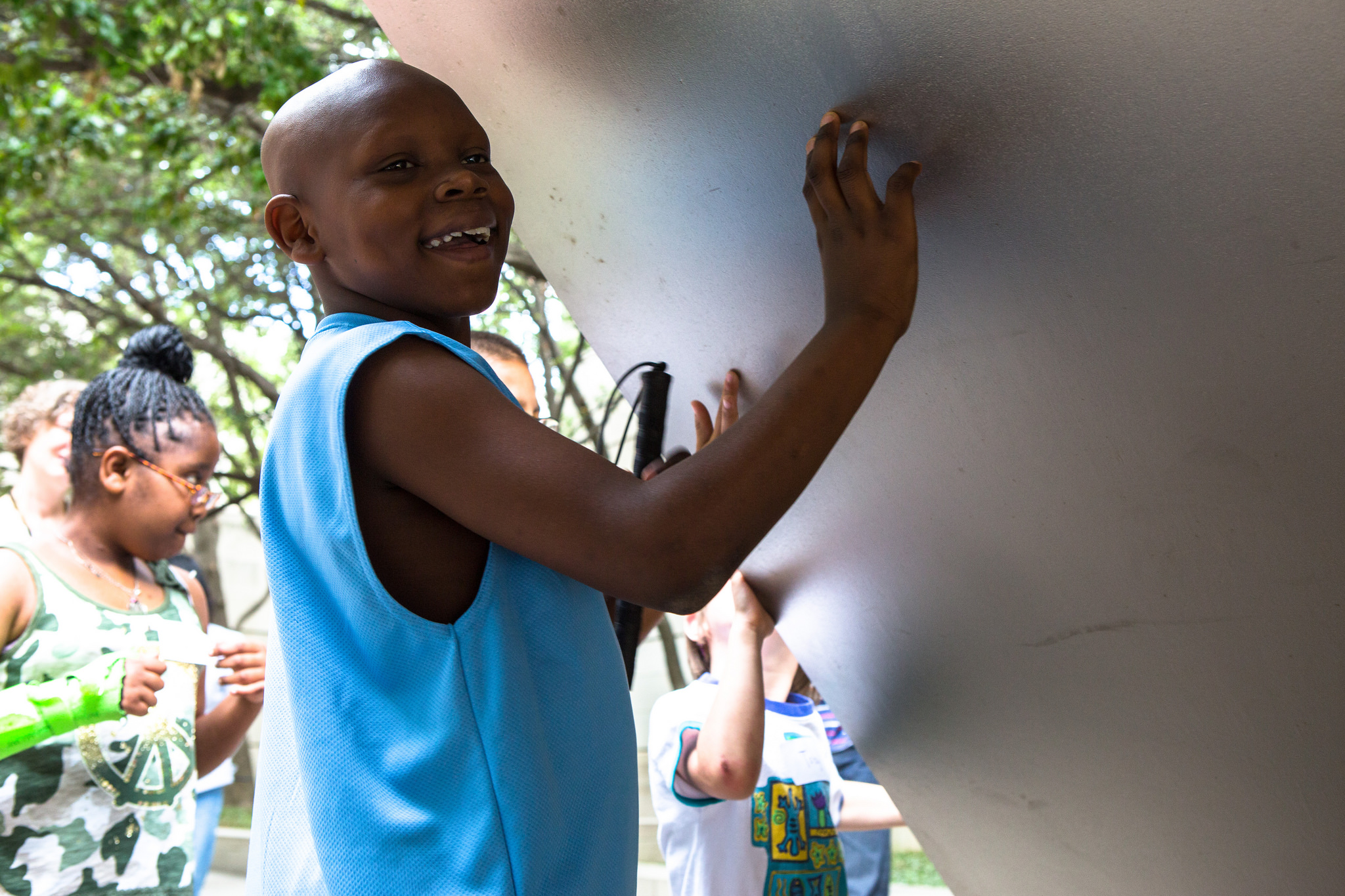Many people may not think that of an art museum as the ideal field trip location for a group of children with visual impairment, but when the Dallas Independent School District (DISD) contacted the DMA earlier this summer with such a tour request, we were eager to provide the best experience possible. When discussing the visit with vision teachers at DISD, they felt it was important to expose their students to art and wanted an experience that would illustrate to the students that they too have the ability to create and appreciate art just as well as any other student.
The Planning Process
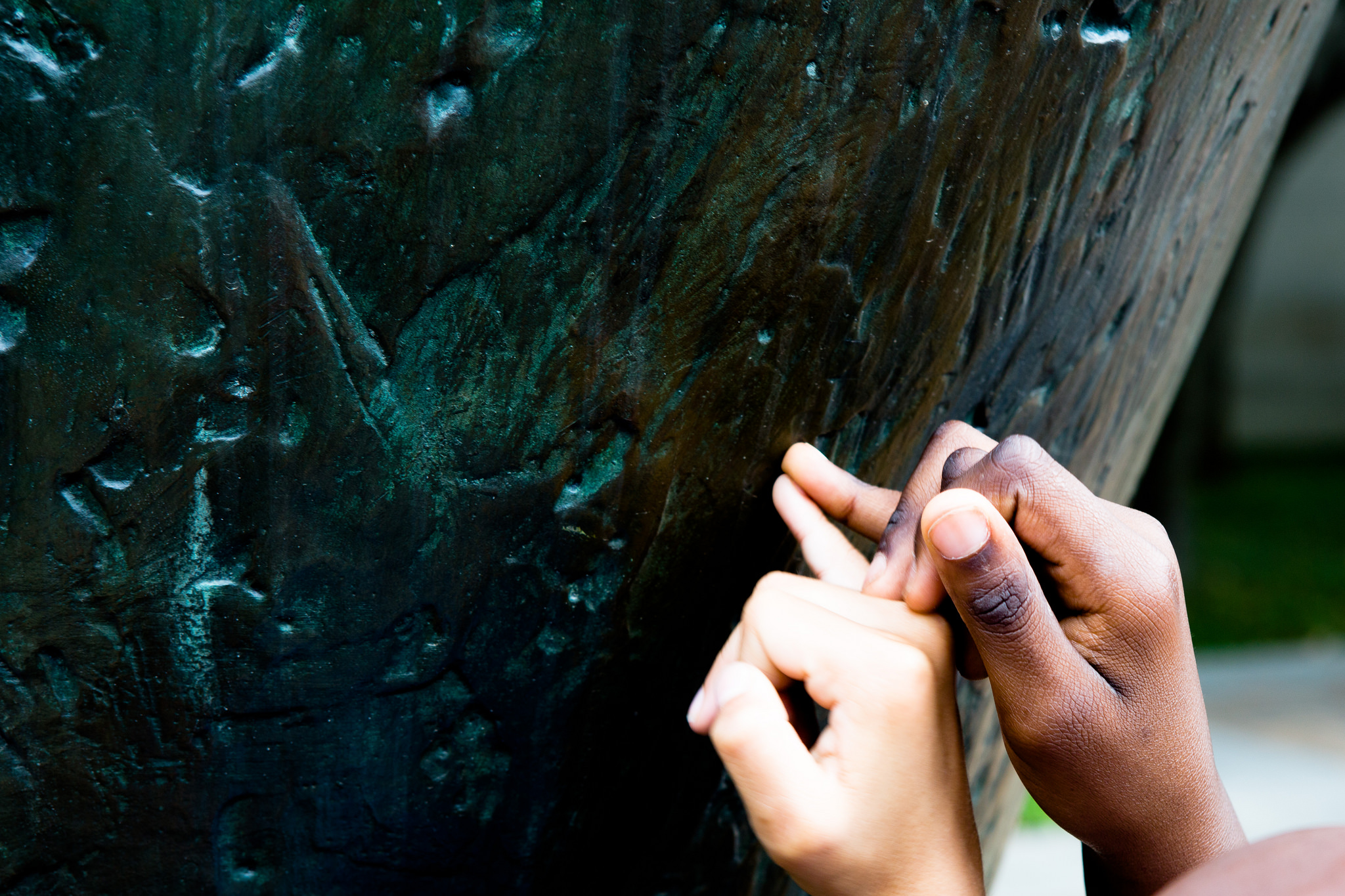
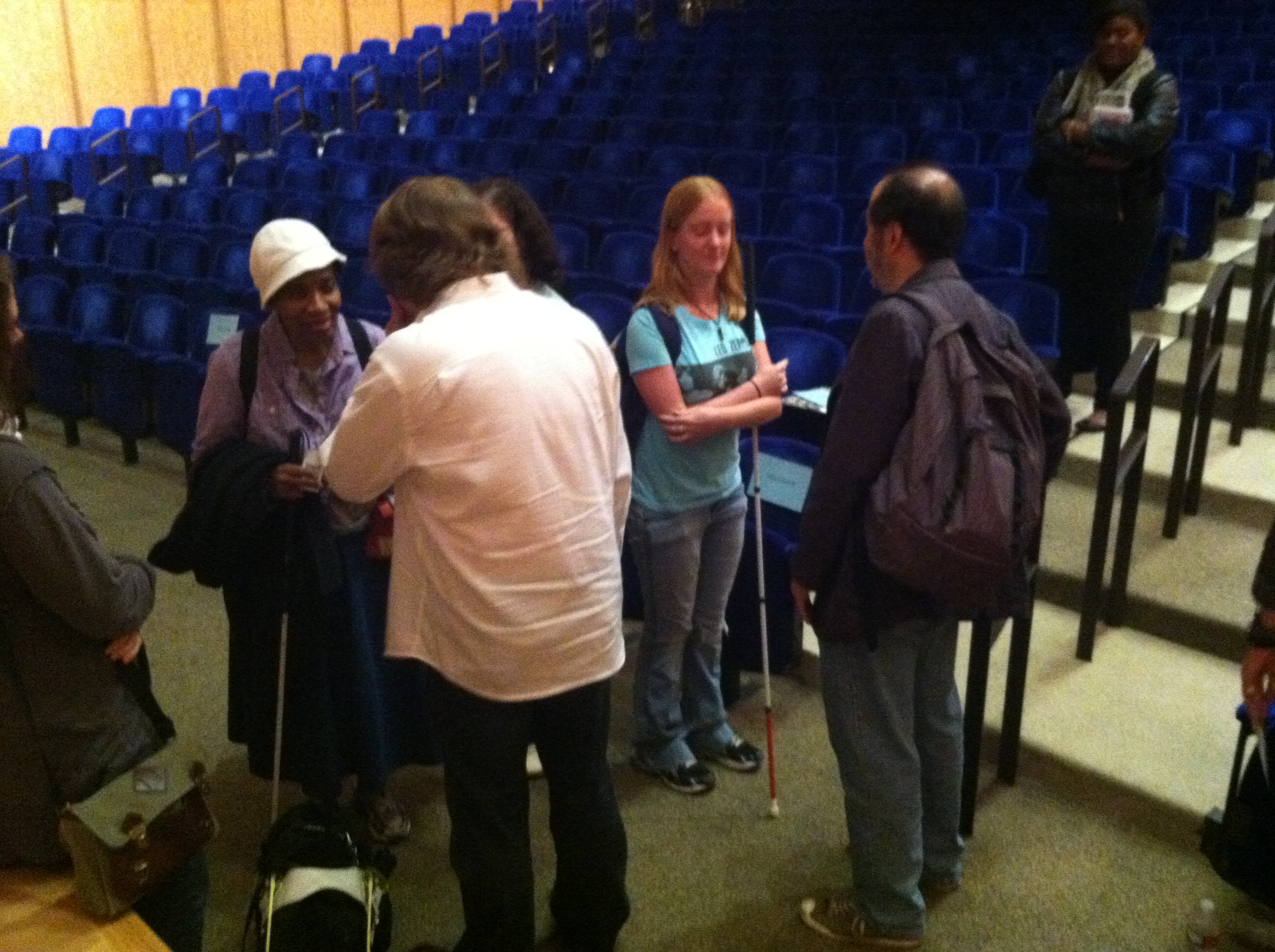
The Dallas Museum of Art has never before offered guided touch tours to visitors with visual impairment, but after speaking with our Director of Exhibition Design, we learned that she fully supports inclusive gallery teaching, and thus was open to supporting the Museum’s first ever touch tour. We talked with our colleagues in the exhibitions and conservation departments and found that they too were fully supportive of trying out a touch tour with the DISD students. The DMA Sculpture Garden was identified as the best place for our inaugural touch tour, since the objects in the garden are designed for an outdoor space and are thus subject to (and able to withstand) a variety of natural elements. We also felt that it was essential for the students to have the galleries to themselves during the tour, so as not to confuse other visitors about the acceptability of touching works of art, as well as for the overall comfort of the students with vision impairment. We therefore decided to schedule the touch tour for a Monday, when the Museum is closed to the public.
Our next step in the planning process was to walk through the space as a group, making note of areas that may be problematic for someone with vision impairment to navigate. The team was comprised of education, conservation, and exhibitions staff, and everyone on the team raised thoughtful questions and contributed wonderful ideas! We discussed which works of art may be the best for a tactile experience, and our conservators suggested that the kids have the chance to touch the works of art without gloves (which is usually unheard of in other touch tours!). Our exhibitions team offered to wash and hand-clean the works we selected so that they would be nice and clean for the experience. And one conservator suggested we select works of art that were large enough to be touched by more than one student at a time, so that the students could talk to one another about what they felt as they each touched the artwork.
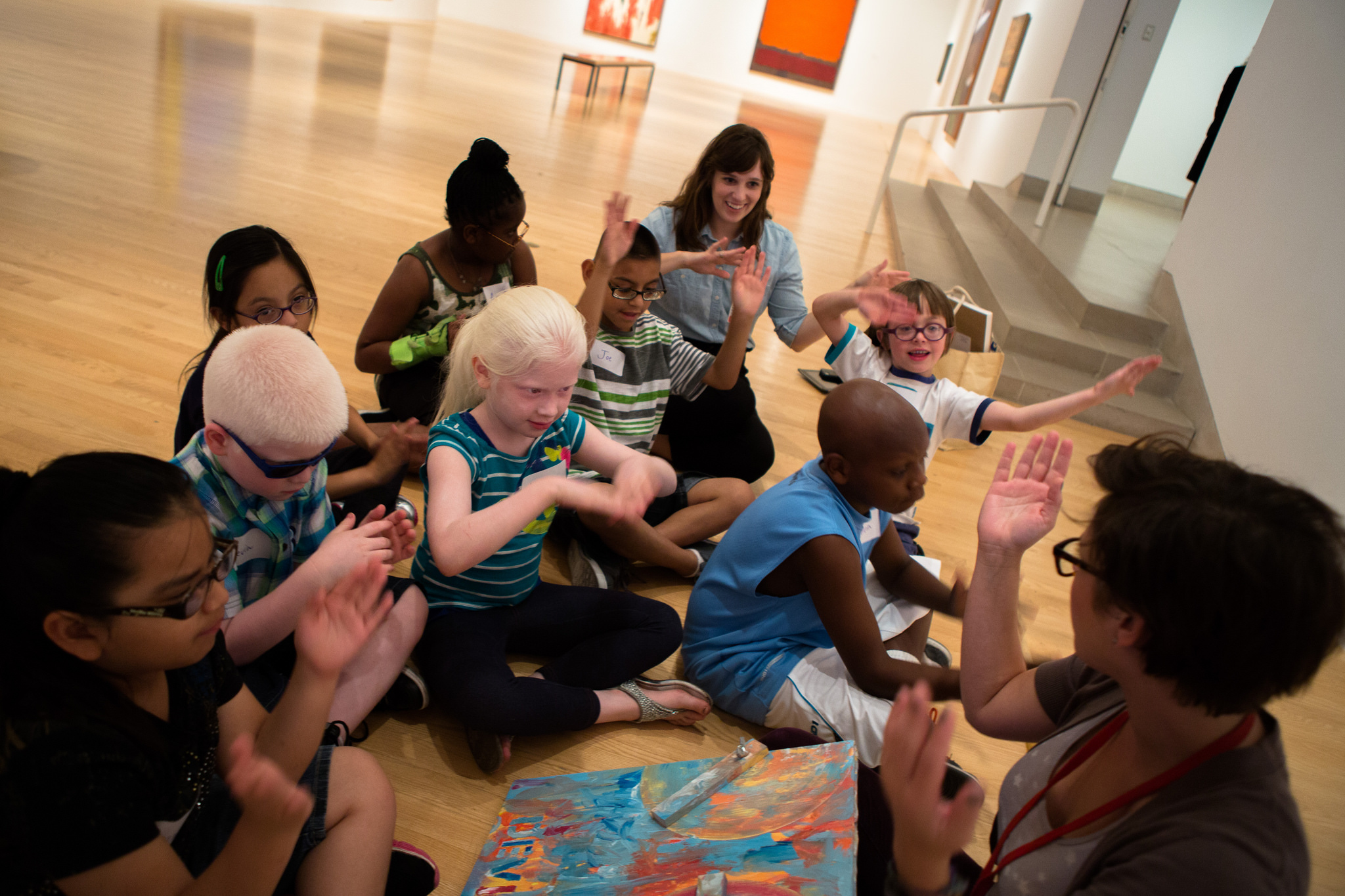
After squaring things away with the exhibitions and conservation teams, the education team began planning the educational experiences of the tour. We prepared for twenty-five students, ranging in age from six to thirteen years, all with a range of visual impairment. The majority of students in the group had some residual vision, while two students were very photophobic, and two were blind from birth. Due to the range of abilities of our tour group, our education team knew it was important to include a variety of artworks in the tour (in addition to those on the touch tour), integrate many descriptive explanations of works of art and hands-on activities, and to have numerous tactile objects available.
In the Galleries
When designing the overall tour, we selected a variety of objects that spanned time periods, artistic techniques, and geographic locations. We visited two contemporary art sculptures in the Sculpture Garden for the touch portion, two Abstract Expressionist works in the contemporary gallery, and a mask in the African gallery. Our aim was to engage all of the senses throughout our tour, as we believe that presenting multiple representations of content would effectively cater to the different learning styles of the group. We created a multi-modal experience by collecting auditory clips for sound stimulation, tactile materials and replica objects for touch, Jelly Belly jelly beans for taste sensations, and essential oils and scented colored pencils for olfactory information.
- Touch tour with Ellsworth Kelly sculpture
- Touch tour with Barbara Hepworth sculpture
- Feeling textures in a Barbara Hepworth sculpture.
- Touch tour with Ellsworth Kelly sculpture
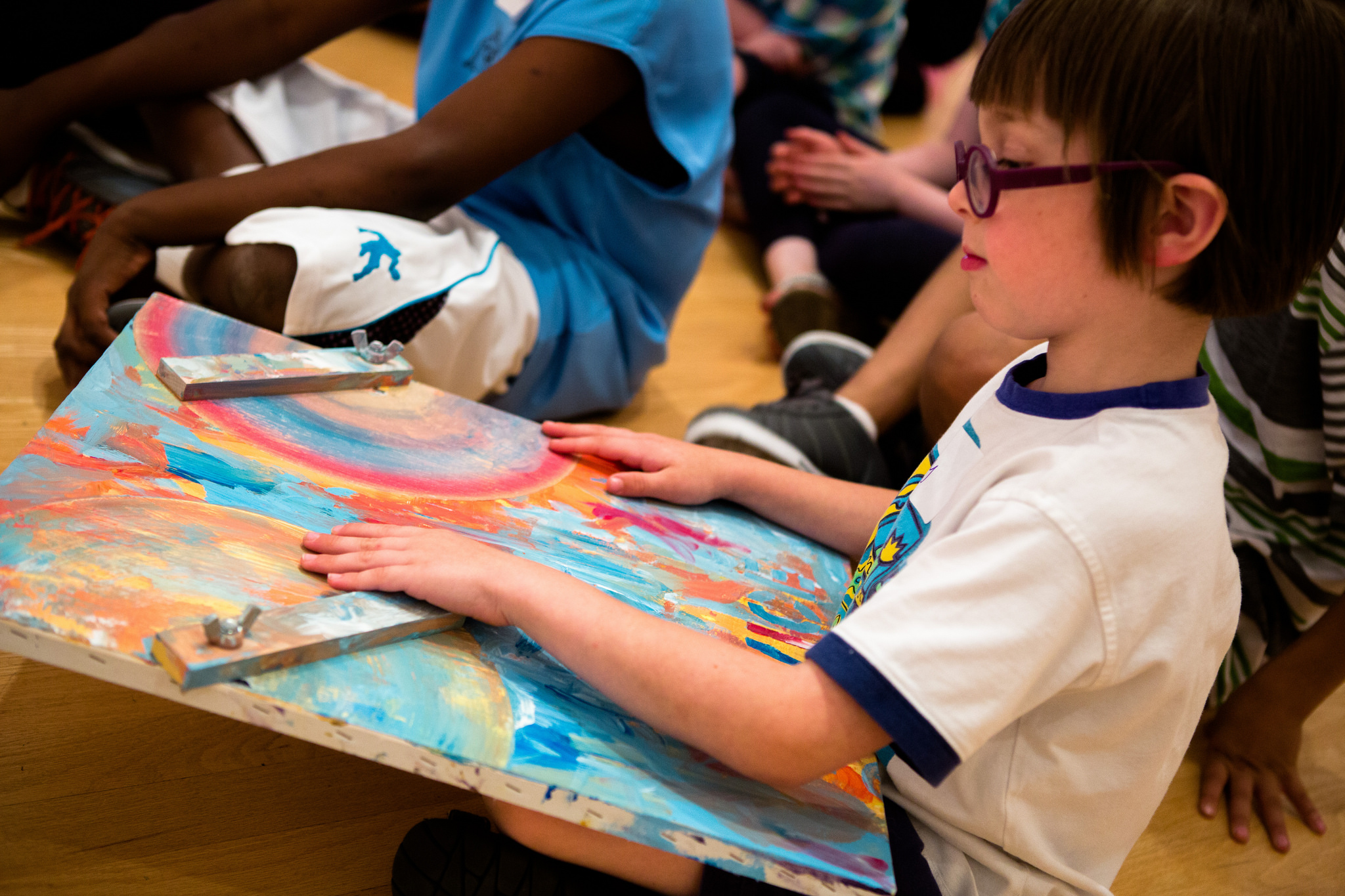
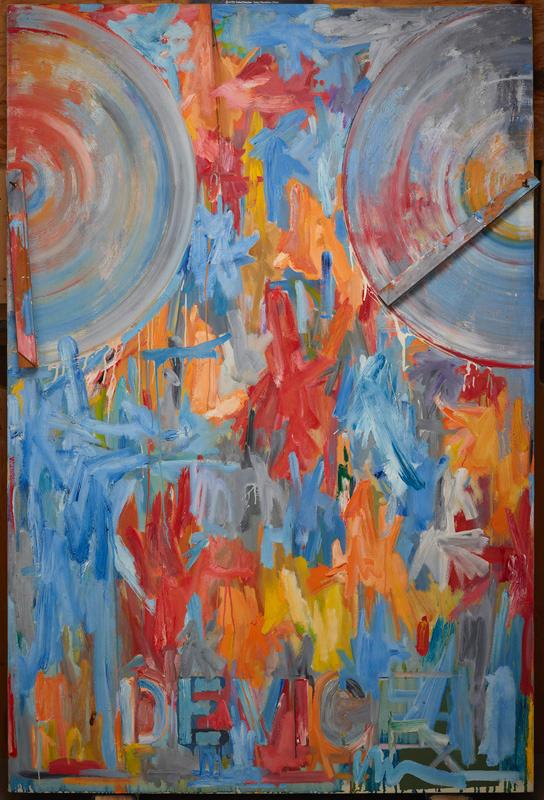
Each stop on the tour had a visual description of the gallery space and of the works of art we focused on, because it was important for us to situate ourselves, the children, and the art in space, as the sense of bodily awareness in space is something that many people without vision impairment may take for granted. Much of our time in the galleries was spent guiding students in tactile looking activities connected to specific works of art and facilitating conversations about texture and form. For instance, we created a reproduction of Jasper John’s Device so that the students could not only touch canvas and feel layers of paint, but they could also replicate moving the wooden stretchers back and forth across the canvas, while imagining the technique in which Johns spread the paint back and forth.
- Recreating the movement in Jasper Johns “Device”
- Feeling the texture of canvas and paint
- Jasper Johns, Device, 1961-1962, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of The Art Museum League, Margaret J. and George V. Charlton, Mr. and Mrs. James B. Francis, Dr. and Mrs. Ralph Greenlee, Jr., Mr. and Mrs. James H. W. Jacks, Mr. and Mrs. Irvin L. Levy, Mrs. John W. O’Boyle, and Dr. Joanne Stroud in honor of Mrs. Eugene McDermott
In the African galleries, we focused on a helmet mask made by the Kuba people of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and passed around raffia, cowrie shells, feathers and other materials found in the mask. Additionally, we played sound clips of the various animals that related to the mask.

Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kuba peoples, Helmet mask (mukenga), mid-20th century, Dallas Museum of Art, gift in honor of Peter Hanszen Lynch and Cristina Martha Frances Lynch
Relating to Richard Diebenkorn’s Ocean Park No. 29, we discussed how an artist could depict a place using sounds, smells, and taste. The students each ate a jelly bean and imagined the color they believed the flavor might represent. Next, they used a scented colored pencil to illustrate a place based on that smell. We also played sound clips of ocean waves and boat horns to recreate the Santa Monica locale that inspired Diebenkorn’s Ocean Park series.

Richard Diebenkorn, Ocean Park 29, 1970, Dallas Museum of Art, gift of the Meadows Foundation, Incorporated
Our tour concluded with a sensory drawing activity that took place at the large fountain outside the Museum’s Flora Street entrance. The students listened to the sounds created by the water in the fountain, and considered how the water (and space around it) might appear, what color the water would be, even how the smell would be rendered. We gave each student a piece of thin Styrofoam and a pencil to create their drawing of the fountain; the students were able to feel the indented lines they drew onto the Styrofoam and took turns sharing their creations with one another.
Until Next Time
This was an exceptional experience for DISD students, teachers, and DMA staff alike. One teacher who helped to organize this visit said that this experience “might be the only time this whole summer [the students] get this opportunity to learn tactually, through their auditory channels and their residual vision, which sighted people take so much for granted.” It was a transformative experience as well for our Museum. We are honored to have been a part of this experience, and cannot celebrate enough the fantastic support and collaboration exhibited by DMA staff from many different departments. A huge thank you to DISD for bringing their students, and a thousand thank you’s to the DMA’s conservation, exhibitions, visitor services, and security teams. This was a team effort and we appreciate the unified support and assistance—let’s hope this is the first of many touch tours to come!
Amanda Blake
Head of Family, Access, and School Experiences
Danielle Schulz
Teaching Specialist