Nicolaus Copernicus was a cleric, a physician, a mathematician—a real renaissance man. Literally. But the true passion that drove him was astronomy. Throughout his life, he took every opportunity to observe the sky and the stars, making meticulous calculations of their positions at a time before the telescope had even been invented. With this detailed data, Copernicus formulated a new theory placing the sun at the center of the universe—an idea that helped to ignite the Scientific Revolution.
Like Copernicus, the Maya were astronomically-minded. Without the benefit of telescopes and other modern advances, they built monumental structures at sites like Chichén Itzá in perfect alignment with the sun during important days of equinox and solstice. Their calendars were also based on the movements of the sun and moon. Their myths and rituals share this cosmological focus, which permeated their entire culture. Even their artworks reflect their celestial mindset.
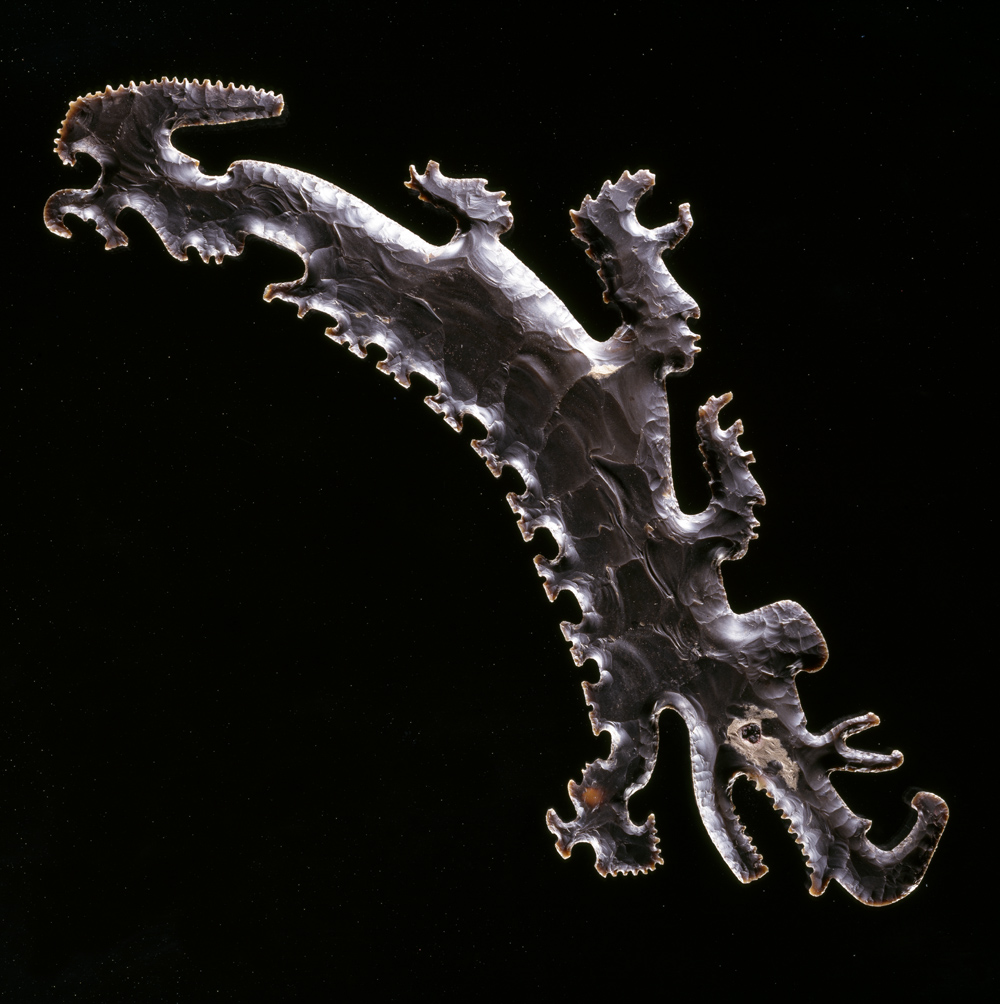
Eccentric flint depicting a crocodile canoe with passengers, Mexico or Guatemala, southern Maya lowlands, Maya, c. A.D. 600-900, The Eugene and Margaret McDermott Art Fund, Inc., in honor of Mrs. Alex Spence.
This flint, shaped like a crocodile canoe carrying its passengers in profile, captures a scene from the Maya creation story. The Maya believed the soul of the First Father was paddled in just such a canoe to the underworld, after which he was reborn as the Maize God, the ancestor of all humans. Contemporary archaeologists have dated this event to August 13, 3114 B.C., based on the Maya calendar. This event was reflected in the heavens each year on August 13, when the Milky Way could be seen floating across the sky from east to west until midnight, when it shifted downward, north to south, plunging into the underworld.
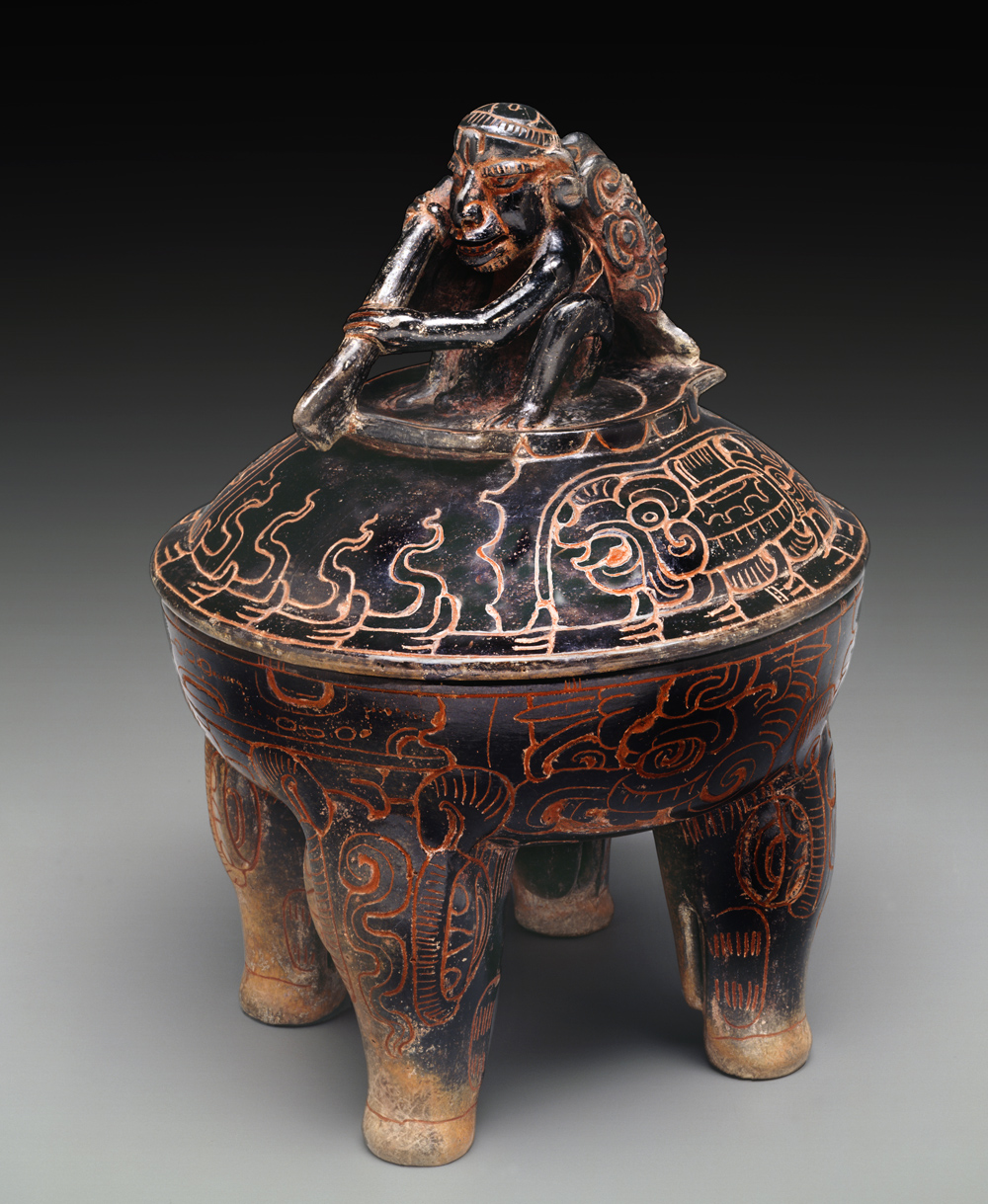

Lidded tetrapod bowl with paddler and peccaries, Mexico or Guatemala, southern Maya lowlands, Maya, c. A.D. 250-550, The Roberta Coke Camp Fund.
Atop this lidded bowl sits the Maya sun god, Kinich Ahau, also in a canoe. As he paddles through the underworld each night, his path takes him through the constellations, one of which is represented by the pig-like mammals incised into the bowl’s legs.
Next Monday, October 24, Arts & Letters Live will welcome author Dava Sobel, whose new book A More Perfect Heaven recounts the revolutionary life and work of Nicolaus Copernicus. Had he been around to observe the skies of ancient America with the Maya, I think they might have found some common ground.
Sarah Coffey
Assistant to the Chair of Learning Initiatives
I think that this flint is one of my favorite pieces in the collection. It is so interesting, both historically and visually. Thanks for sharing Sarah!