Tomorrow evening the DMA will kick off an Annual Fête celebrating 18th-century French masterpieces from the Michael L. Rosenberg Collection and the release of a new publication, French Art of the Eighteenth Century: The Michael L. Rosenberg Lecture Series at the Dallas Museum of Art. Join us for performances, talks, art making, and a tres magnifique menu.
Before we step back in time and party like it’s 1799, I asked each of the past and present curators of the Rosenberg Collection to share a favorite work of art or a fond memory of working with this group of objects. Catch up with them at the Annual Fête, where they will be available to answer questions about your favorite Rosenberg artworks.
Nicky Myers, The Lillian and James H. Clark Curator of European Painting and Sculpture, DMA
“It is truly a privilege to be able to display and study such an important collection of 18th-century French artwork. Beyond its art historical significance, beyond its extraordinary quality and condition, the Rosenberg Collection is simply stunning. Lush colors, sumptuous costumes, and elegant figures welcome you to the Michael L. Rosenberg Galleries of 18th-Century Art, some of my favorite rooms in the Museum. When we enter these spaces, we are instantly transported back in time to a rare moment when the decorative and fine arts shared the same aesthetic, and when patrons and artists shared similar sensibilities. It is hard for me to choose a favorite work within the Rosenberg Collection, but I’m particularly drawn to the Greuze, Boilly, and Largillière paintings.”
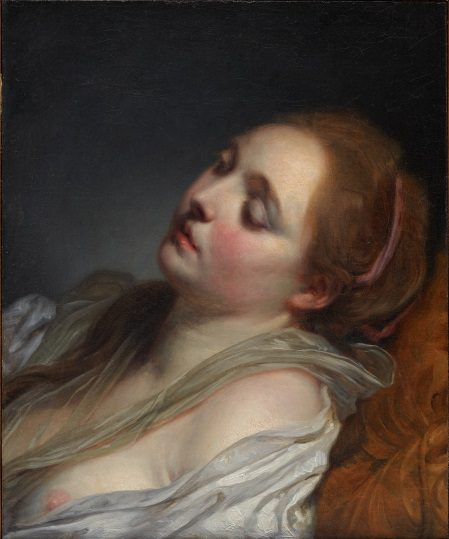

Jean-Baptiste Greuze, The Dreamer, 1765–69, oil on canvas, lent by the Michael L. Rosenberg Foundation, 29.2004.10
Heather MacDonald, Program Officer, Getty Foundation
“What I enjoyed most about working with the Michael L. Rosenberg Collection and its annual lecture series was the opportunity to invite amazing scholars, whose work I’ve admired for years, to come to Dallas and share their research. They’re like historical detectives, piecing together bits of evidence gathered over a lifetime of research and close looking.
I don’t like to choose favorites among works of art in the galleries, but I will confess to an adoration of François-André Vincent’s portrait of the playwright Desforges. It’s such a modern, informal portrait: Desforges is shown in his (beautifully painted) shirtsleeves, with a five-o’clock shadow, looking off in the distance as if caught in a moment of creative inspiration. Vincent painted Desforges on the cusp of the Revolution, which offered new kinds of individual freedoms to French citizens, but this portrait also says so much about how the modern individual had been reimagined by the Enlightenment. There is a whole story about the 18th century contained in this image!”
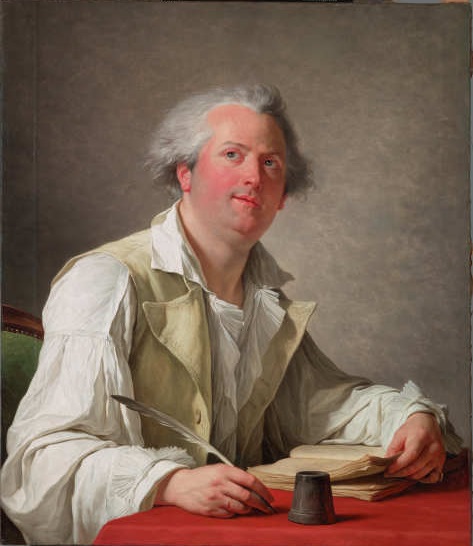

François André Vincent, Portrait of Pierre-Jean-Baptiste Choudard (called Desforges), 1789, oil on canvas, lent by the Michael L. Rosenberg Foundation, 29.2004.1
Eik Kahng, Assistant Director and Chief Curator, Santa Barbara Museum of Art
“What I remember most fondly about Michael was his sincere love for the works of art that he collected. Before it came to the DMA, the collection was installed at Michael’s house. He very kindly allowed for private tours from time to time, which everyone greatly enjoyed. Michael would routinely ask me to lead the tours, starting in the living room, where the great Lemoyne Bather and the wonderful Oudry animal painting of a water spaniel confronting a heron were on view. However, about five minutes into my talk, Michael would invariably interrupt and start adding his own, detailed commentary. He was so passionate about each and every object and could speak eloquently and informatively about each one. I always teased him that he didn’t need me to be there at all, since he was more than capable of providing his own overview of the collection. It’s always such a pleasure to listen to collectors who really love their art.”

Jean–Baptiste Oudry, Water Spaniel Confronting a Heron, 1722, oil on canvas, lent by the Michael L. Rosenberg Foundation, 29.2004.8
Jessie Frazier is the Manager of Adult Programming at the Dallas Museum of Art.