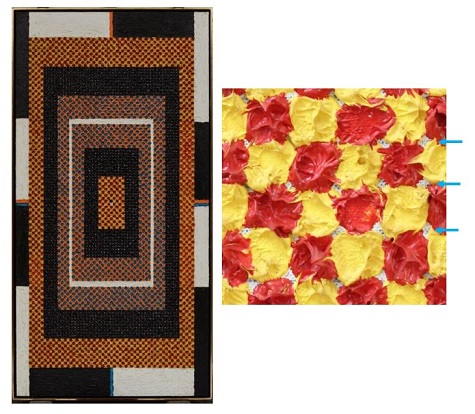
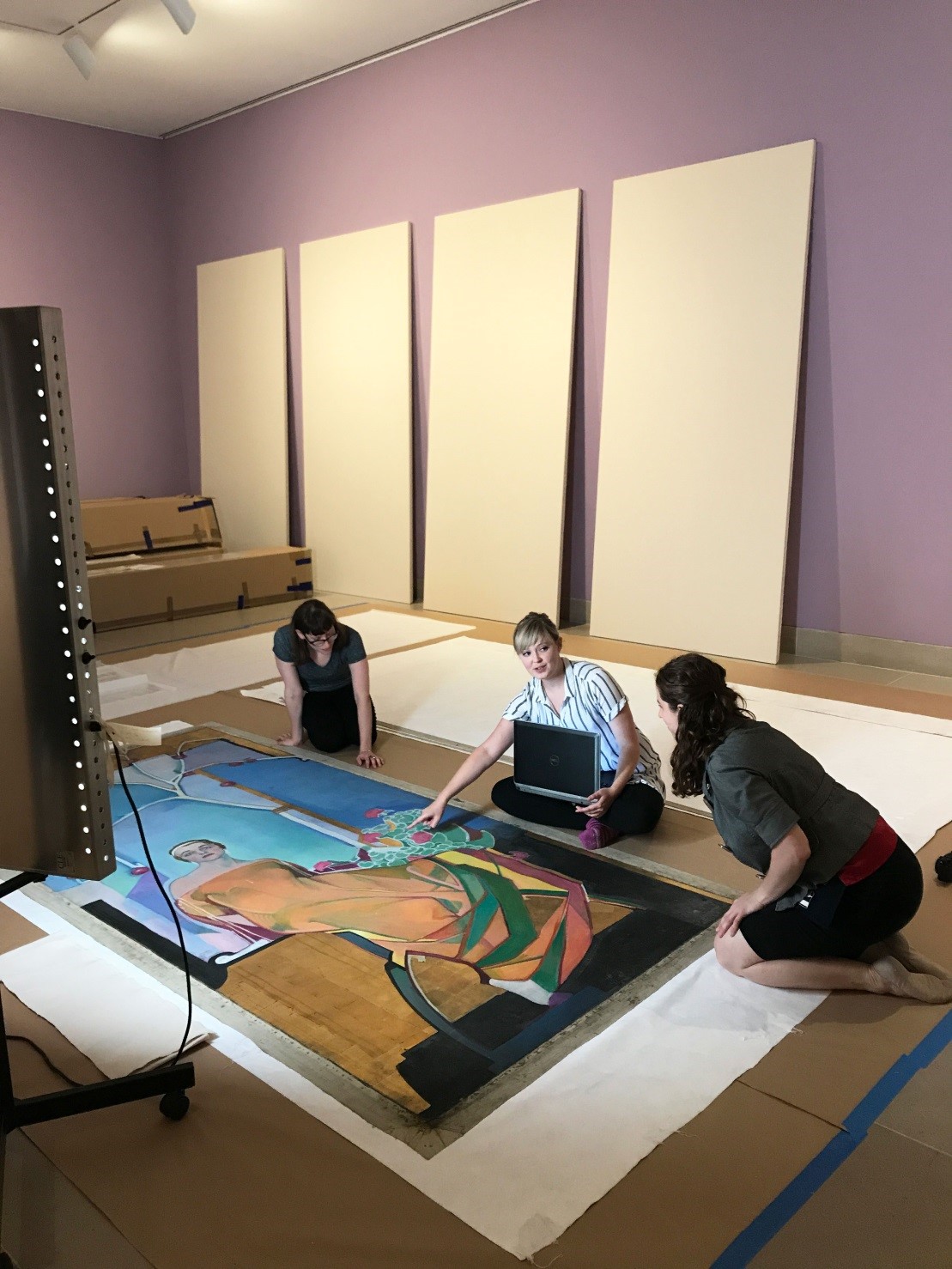
Mathematics and art, two subjects that are often thought of as an unlikely combination; however, for American artist Alfred Jensen these two subjects fit together exactly. One of Jensen’s geometric, mathematical paintings could be seen if you peeked into the Conservation Studioab this past fall. This painting may appear simple in design, but the process and the surface are very complicated and interesting. Jensen was fascinated by the Maya calendar, philosophy, mathematics, color theory, pre-Columbian culture, and Asian culture. All of these things influence the compositions he creates, and in this particular painting there is very likely a specific reason for the number and placement of each dot of paint throughout the work.
Jensen combines mathematical and philosophical theory with artistic practice in his works similar to the way the field of conservation combines science with art. This perfect comparison makes it all the more exciting to perform a conservation treatment on this painting. In this work, it appears that Jensen applied the paint straight from the tube by dotting it directly onto a primed canvas. The dots were clearly not added at random, but were planned out, as is evidenced by a grid applied in pencil that can be seen in the reserves between the dots, below the paint.
Due to the high impasto of each little dot of paint, little cups and horizontal platforms are created that are perfectly positioned for catching and gathering dust. The dust detracts from and changes the way the colors interact with each other, affecting the color theory aspect of Jensen’s technique. Additionally, since the surface is unvarnished, the dust has started to attach itself to the paint, which will make it increasingly difficult to remove in the future.
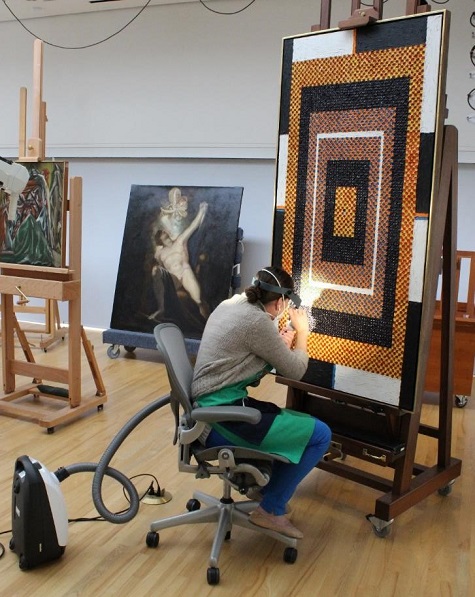
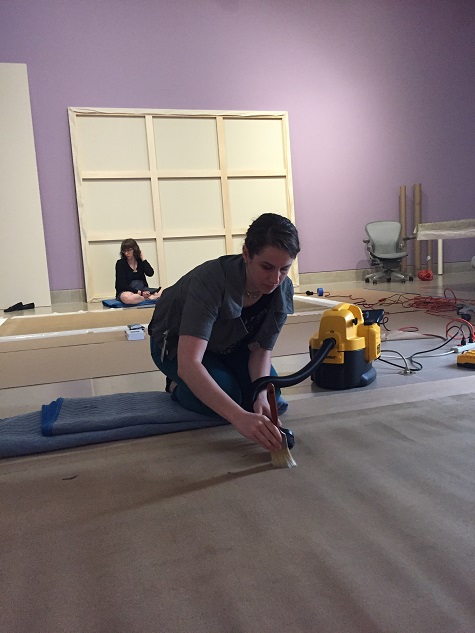
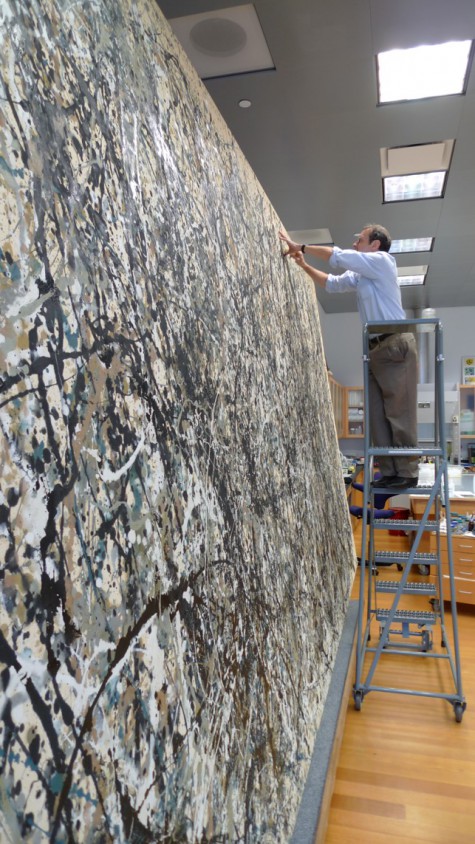
Removing the dust from the surface is no easy task. Each little dot of paint has pointed ends that are extremely fragile and sometimes very small and difficult to see without magnification. As the DMA’s conservation intern, I began cleaning this painting in September 2017. In the image below, I’m using an optivisor to be able to see the very tiny, vulnerable peaks of paint and a small, soft brush to carefully dust each daub of paint to reveal the intended color below without disturbing the peaks. A HEPA vacuum gathers the dust so it doesn’t settle back onto the paint below.
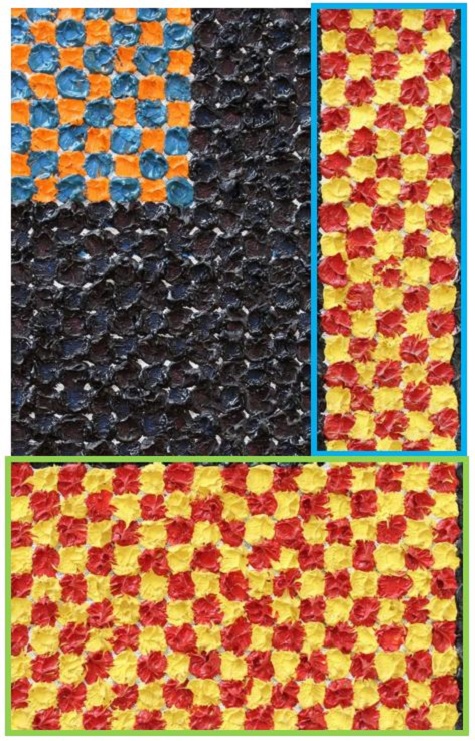
The removal of the dust is a very slow, careful process because each little dot essentially becomes its own painting, requiring individual attention. From the viewing window of the Conservation Studio, it may seem as if the painting has not changed very much; however, below you can see the difference between a cleaned (green) and uncleaned area (blue) of the painting. The area in the green square is no longer dull and gray, and the colors show their intended vibrancy. The cleaning, while slow and detailed, is a very satisfying process.
Caroline Hoover is the Conservation Intern at the DMA.