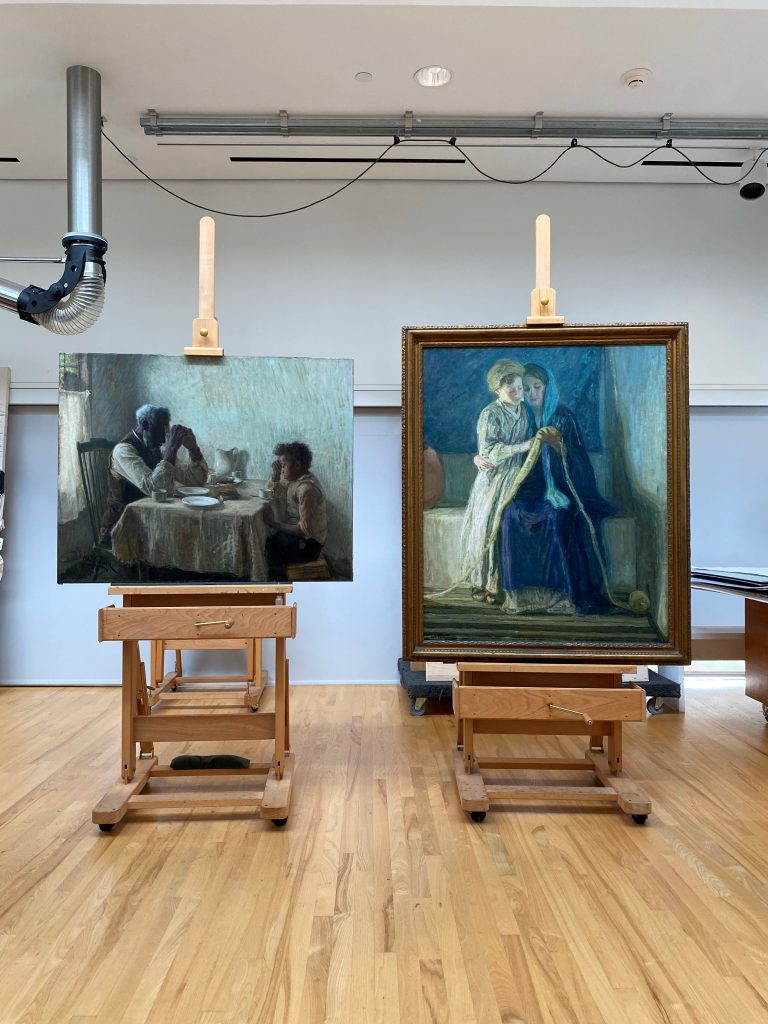
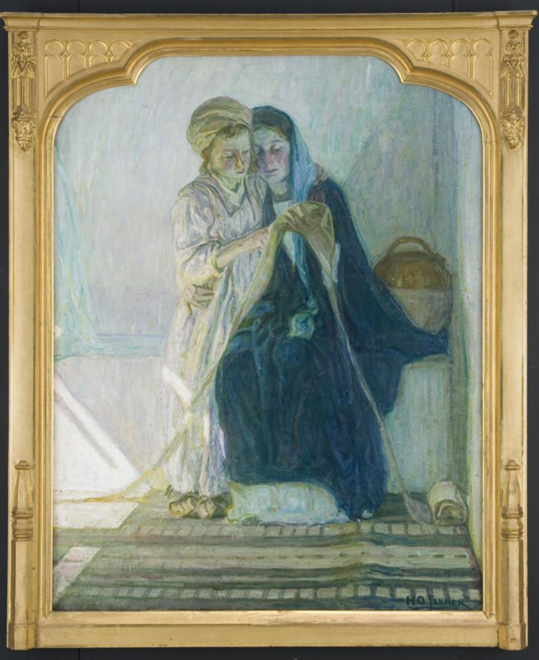
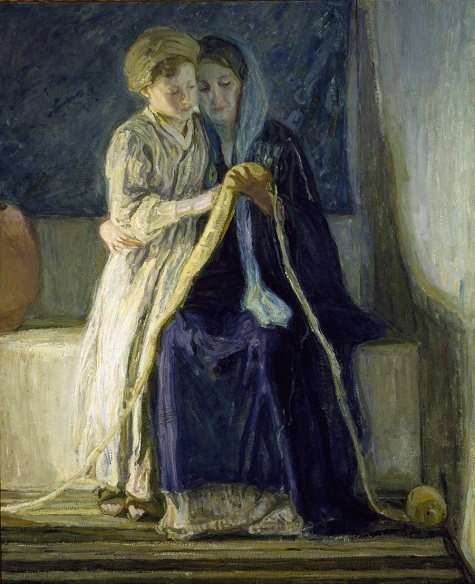
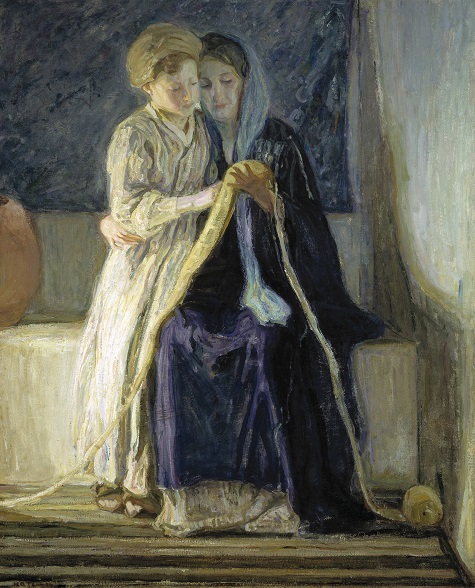
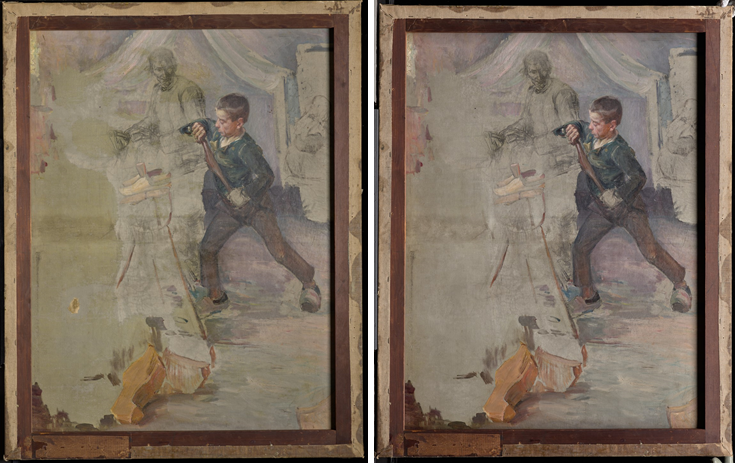The Dallas Museum of Art and Art Bridges Foundation partnered in early January of this year to undertake the conservation treatment and technical study of Art Bridge’s newly acquired masterpiece The Thankful Poor by Henry Ossawa Tanner. Additionally, the project will allow for the first public presentation of the work, curated by Sue Canterbury at the DMA.

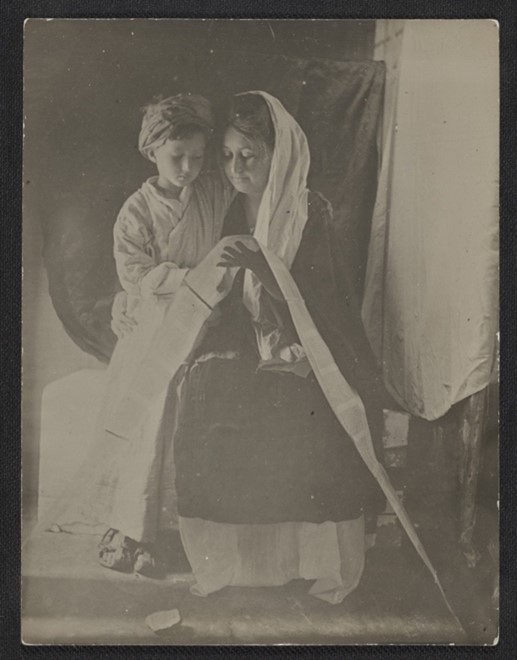
When The Thankful Poor arrived at the DMA’s conservation studio, it was already strikingly beautiful. The composition holds space and immediately draws the viewer in. The painting is double-sided, presenting an unfinished version of The Young Sabot Maker on the reverse, a composition Tanner would complete the following year and which now resides in the Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art’s collection.
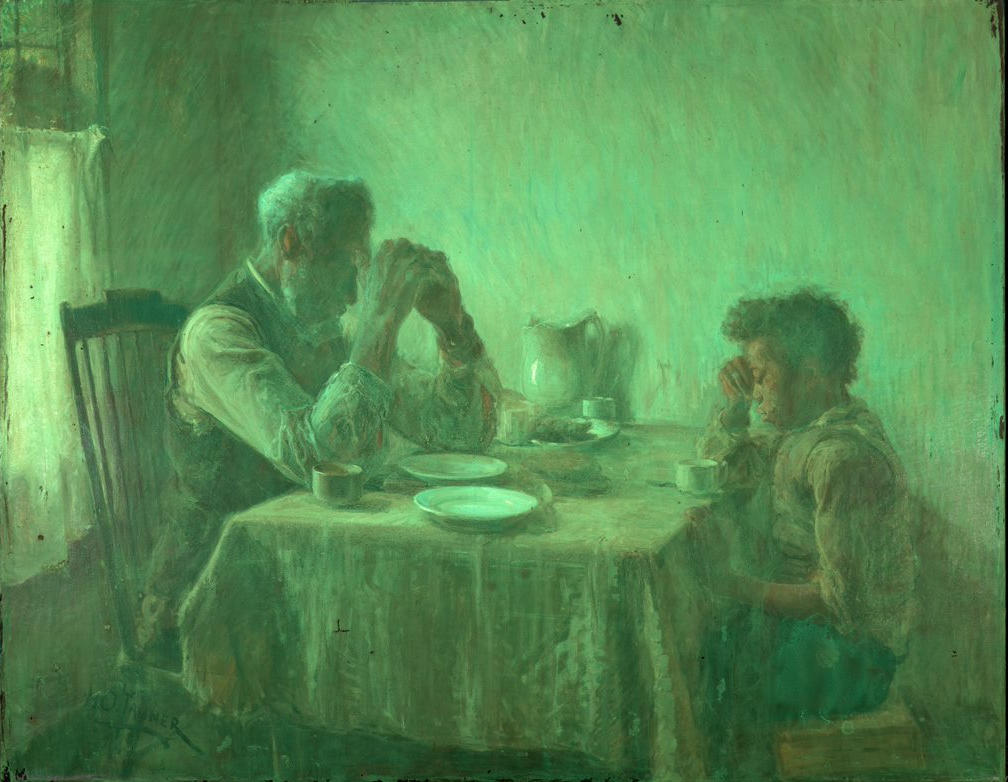
Prior to any conservation treatment, a thorough examination is always undertaken, including archival documentation research relating to any previous interventions. It became apparent that the work had undergone at least one relatively minor restoration campaign in the 1970s. It was also evident that the painting was cleaned and re-varnished in a second treatment, though no verifiable documentation was found. UV illumination was used to better understand which varnishes and treatment materials might have been used, as surface materials such as varnishes and areas of retouching can be differentiated based on their observed fluorescence. In this painting, the varnish is seen glowing green, and older areas of restoration present as black spots.

As both of these treatments took place many years earlier, the varnish layers had become discolored, both yellowed and cloudy. An old tear that had been repaired using wax and paper had also begun to open and needed to be addressed. Finally, a thick layer of discolored adhesive was scattered throughout the composition on the reverse of the canvas.
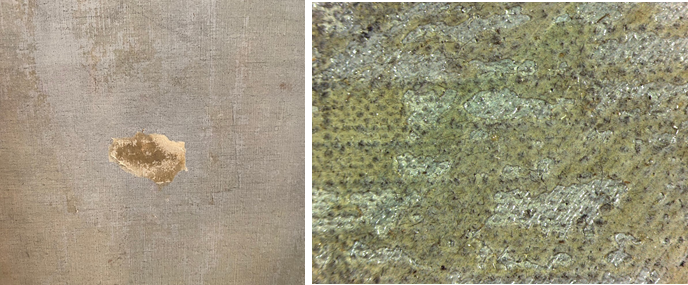
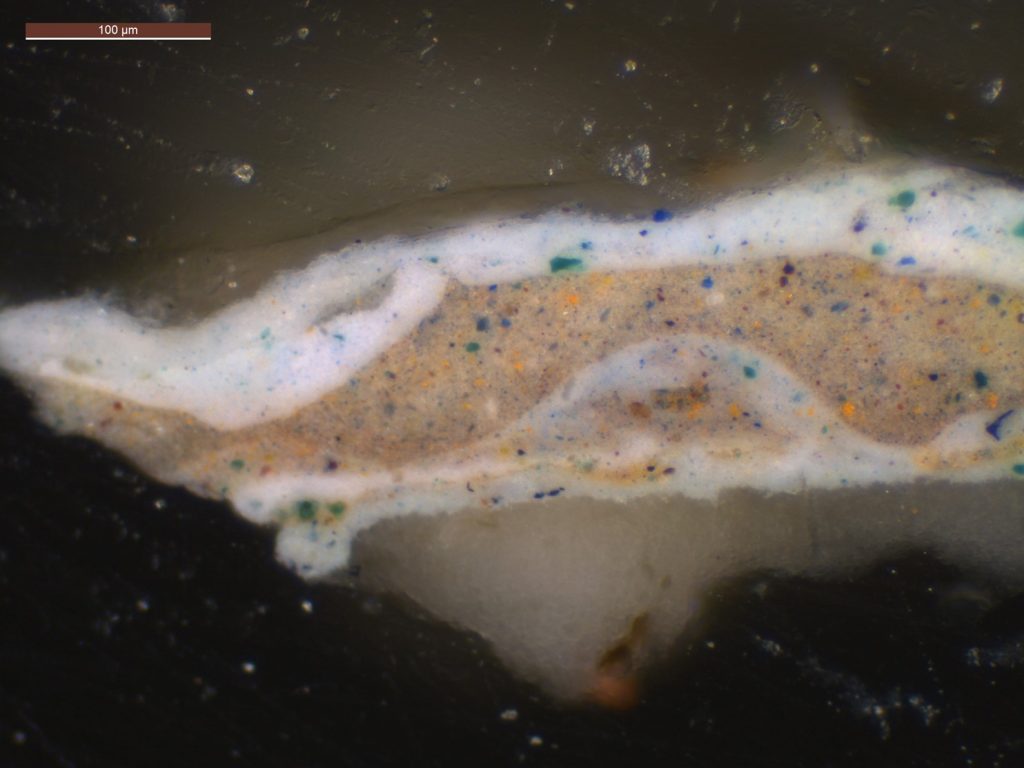
Tanner was an innovative artist, known to experiment with layering techniques that require especially mindful cleaning approaches. Cleaning tests were conducted under microscopic magnification to determine a cleaning protocol to remove the layers of discolored varnish. To better understand the boundary between paint and varnish, a microscopic sample was used to gain a view of the various layers. The resulting cleaning process was executed almost entirely under the microscope to ensure the most delicate layers were preserved.
The tear was then mended and areas of losses were filled and retouched using reversible conservation materials. Wide cracks, known as traction cracks, were carefully retouched to better integrate the surface visually.
The cleaning was transformative. The layers of discolored varnish lifted to reveal a colorful palette previously unseen. The overall tone of the painting shifted to unveil a much cooler composition, balancing the contrast.
It was an honor to work on this beautiful painting. Results from the treatment allow the work to be appreciated as the artist intended. Tanner was a master of tone and light, both of which he captured so beautifully in this magnificent composition. Research and treatment work were done collaboratively with my fabulous curatorial colleagues, both at the DMA and at Art Bridges, and I want to give a heartfelt acknowledgment to Sue Canterbury, Martha MacLeod, and Margi Conrads for their collaboration.
Laura Eva Hartman is the Paintings Conservator at the DMA.